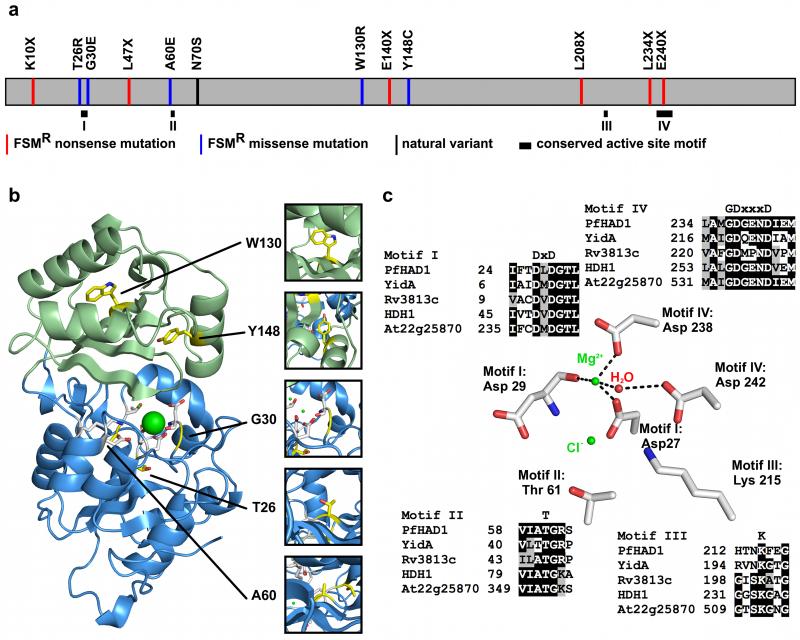
Figure 3. FSMR variants map to the core and active site regions of PfHAD1.
(a) Schematic of PfHAD1 variants found in FSMR strains. Six of the alleles result in premature stop codons. Five alleles produce full-length protein. N70S is a nondeleterious allele reported from sequenced clinical and laboratory isolates. Conserved active site motifs are shown as black boxes25. (b) Overall structure of PfHAD1 with the core domain in blue, cap domain in green, and polymorphic residues mapped in yellow. Residues W130 and Y148 are located in the hydrophobic inner region of the cap domain. Residues T26 and A60 are located in the hydrophobic inner region of the core domain. Residue G30 is located in the substrate-binding site. (c) The backbone carbonyl oxygen of Asp-29 and the side chains of Asp-27 and Asp-238 coordinate a magnesium ion to form the active site. The side chains of Asp-29, Thr-61, and Lys-215 coordinate a chloride ion, and are correctly positioned to coordinate a phosphate group upon substrate binding. These activesite residues are conserved in PfHAD1 homologs from organisms possessing the MEP pathway. Alignment was produced in T-Coffee55 using default parameters. Accession codes for NCBI protein sequences: E. coli YidA, EOU46719; M. tuberculosis Rv3813c, NP_218330; C. reinhardtii FER_156463, ADF43173; A. thaliana At2g25870, ABO38782.