Figure 2. Stability and gene silencing activity of chemically modified siRNA.
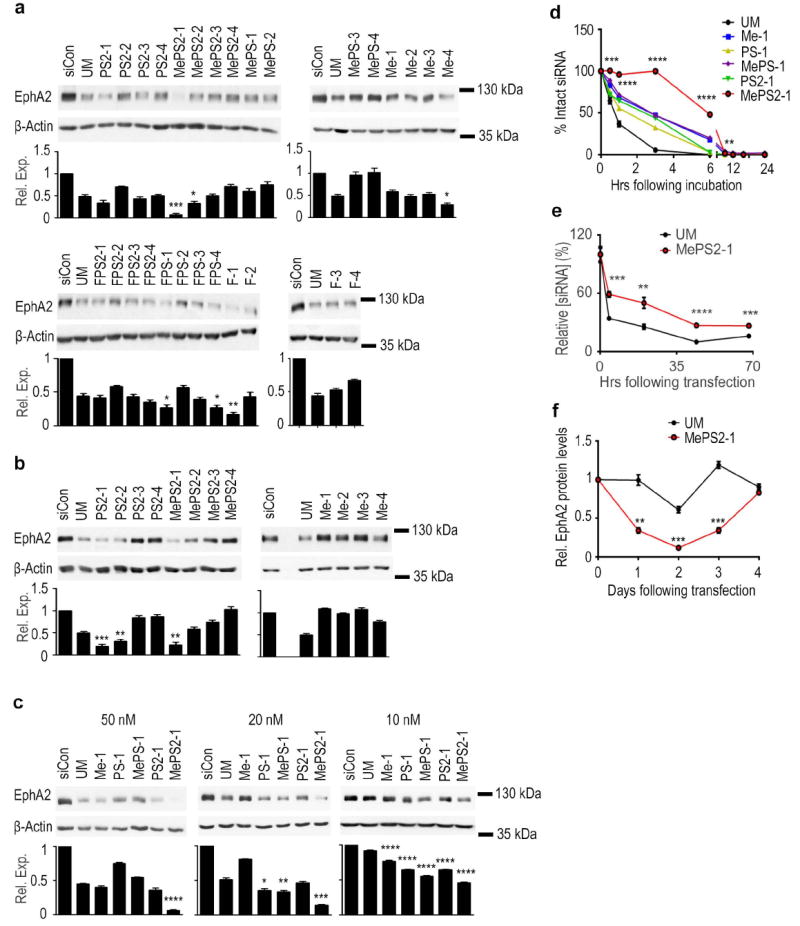
(a) Knockdown of EphA2 in SKOV3ip1 cells using chemically modified siRNAs (100 nM, serum-free condition). (b) Knockdown of EphA2 using selected siRNA sequences in HeyA8 cells (100 nM, serum-free condition). (c) Knockdown of EphA2 using chemically modified siRNAs in SKOV3ip1 cells (10, 20, and 50 nM, 10% FBS-containing media). (a, b, and c) Cells were treated with siRNAs for 4 h and EphA2 protein levels were examined 48 h post-transfection. (d) Stability of chemically modified siRNAs in 10% FBS at 37 °C. (e) Intracellular stability of UM and MePS2-1 modified siEphA2 in SKOV3ip1 cells (50 nM, serum-free condition). (f) Duration of EphA2 knockdown following UM and MePS2-1 modified siEphA2 treatment in SKOV3ip1 cells (50 nM, 10% FBS-containing media). [P-values obtained with Student’s t-test; *, P<0.05; **, P<0.01; ***, P<0.001; or ****, P<0.0001; compared to UM siEphA2 sequence; bars and error bars represent mean values and the corresponding S.E.M.s (n=3)].
