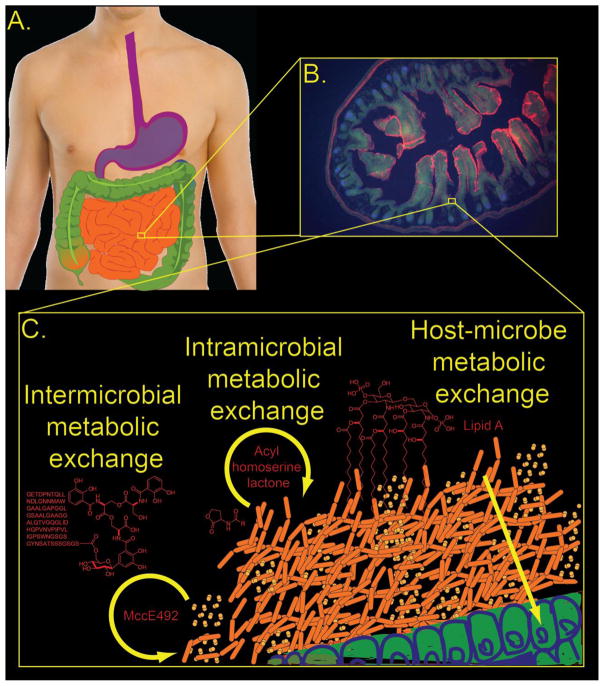
Figure 1. The bacterial chemical repertoire as metabolic exchange factors within the gut microbiome.
A. The human digestive tract is populated by diverse bacteria, forming the microbiome, from esophagus to anus. B. A fluorescence confocal microscopy image of the small intestine. C. A schematic illustrating hypothetical metabolic exchange between host, Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumonia. Metabolic exchange can be intraspecies (e.g. quorum-sensing), interspecies, or host-symbiont communication.