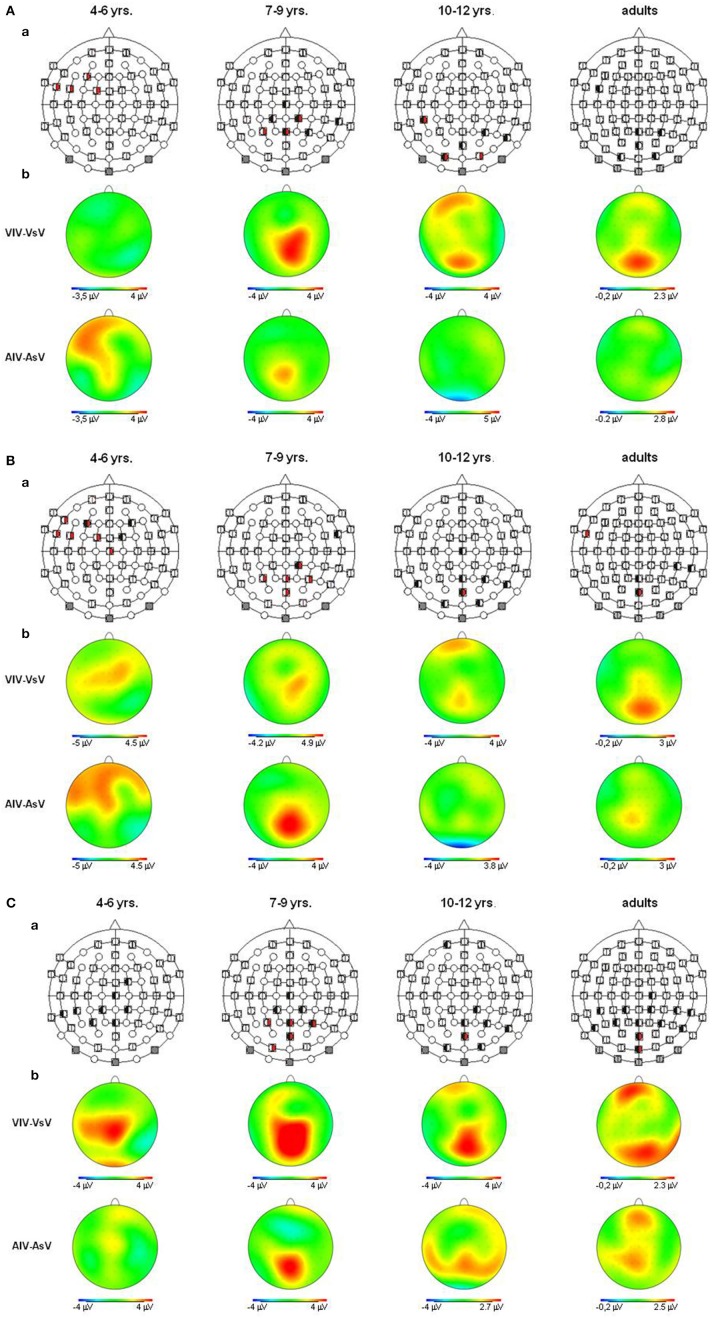
Figure 4.
(A) Visual refractory period effects (p ≤ 0.05) in the unimodal (black, left segment) and the crossmodal (red, right segment) condition, separately illustrated for each age group (a). Voltage difference maps of conditions with a long ISI minus conditions with a short ISI (unimodal vs. crossmodal) (b). Analyzed time windows: 100–150 ms (children), 90–140 ms (adults). Abbreviations: [vsv]: e.g., ERP to a visual stimulus preceded by a visual stimulus with a short ISI: a, auditory; v, visual; s, short ISI; l, long ISI. (B) Visual refractory period effects (p ≤ 0.05) in the unimodal (black, left segment) and the crossmodal (red, right segment) condition, separately illustrated for each age group (a). Voltage difference maps of conditions with a long ISI minus conditions with a short ISI (unimodal vs. crossmodal) (b). Analyzed time windows: 150–220 ms (children), 140–190 ms (adults). Abbreviations: [vsv]: e.g., ERP to a visual stimulus preceded by a visual stimulus with a short ISI: a, auditory; v, visual; s, short ISI; l, long ISI. (C) Visual refractory period effects (p ≤ 0.05) in the unimodal (black, left segment) and the crossmodal (red, right segment) condition, separately illustrated for each age group (a). Voltage difference maps of conditions with a long ISI minus conditions with a short ISI (unimodal vs. crossmodal) (b). Analyzed time window: 260–340 ms in children and adults. Abbreviations: [vsv]: e.g., ERP to a visual stimulus preceded by a visual stimulus with a short ISI: a, auditory; v, visual; s, short ISI; l, long ISI.