Figure 1.
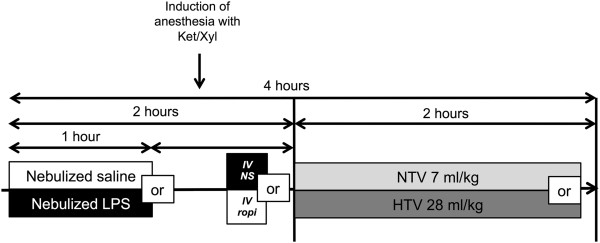
Schematic illustration of the workflow of animal experiments. C57BL/6 mice (WT) were exposed to either normal saline (NS) or nebulized LPS (10 mg) for 1 hour. Induction of anesthesia with ketamine/xylazine (Ket/Xyl) during the second hour of the experiment was followed by the insertion of a central venous catheter into the right or left internal jugular vein and the application of an intravenous bolus of either 0.01 mg ropivacaine (ropi in the figure, R in the group description) or vehicle (normal saline, NS). Mice were then mechanically ventilated for 2 hours via a tracheostomy with either normal tidal volumes (7 ml/kg, NTV) or high tidal volumes (28 ml/kg, HTV). Mice were randomized into 8 different groups (n = 7 each): 1) Nebulized NS, intravenous NS, NTV ventilation (NS-NS-NTV; control), 2) NS-R-NTV, 3) LPS-NS-NTV, 4) LPS-R-NTV, 5) NS-NS-HTV, 6) NS-R-HTV, 7) LPS-NS-HTV, 8) LPS-R-HTV.
