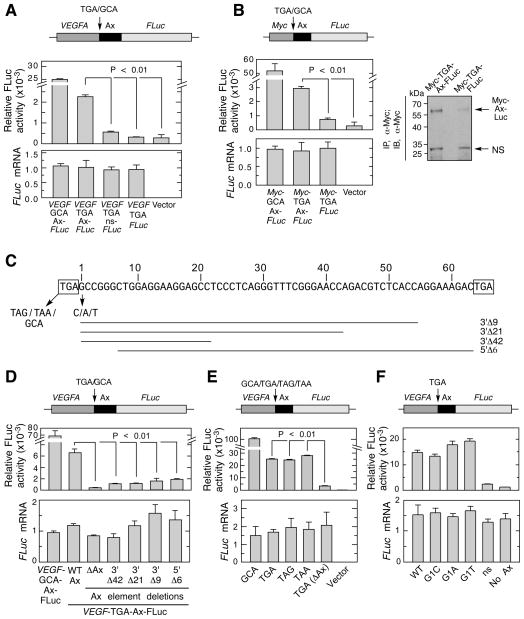
Figure 3. Ax Element is Necessary and Sufficient cis-acting Signal for VEGFA mRNA Readthrough.
(A) Ax element is sufficient for readthrough of VEGFA chimeric transcript. Plasmid containing in-frame VEGF-Ax-FLuc, and variants with TGA-to-GCA substitution, no Ax element, and Ax replaced by a non-specific sequence (ns), were transfected into ECs. FLuc activity was normalized to expression of co-transfected Renilla Luc (top), and FLuc mRNA expression determined by qRT-PCR (bottom).
(B) Ax element is sufficient for readthrough of heterologous mRNA, Chimeric plasmids containing Myc-Ax-FLuc and variants were transfected into ECs. Relative FLuc activity and mRNA expression were measured (left). Readthrough product also was determined by immunoprecipitation with rabbit anti-Myc-tag antibody followed by immunoblot with the mouse anti-Myc-tag antibody (right).
(C) Nucleotide sequence of bovine Ax element. Flanking stop codons (boxes), deletions (horizontal lines) and mutations (arrows) are shown.
(D) Plasmids containing deletions of VEGF-Ax-FLuc were transfected into ECs. FLuc activity was normalized by expression of co-transfected Renilla Luc (top); FLuc mRNA expression was determined by qRT-PCR (bottom).
(E) All three stop codons permit readthrough. ECs were transfected with VEGF-Ax-FLuc constructs containing each stop codon. Relative FLuc activity and mRNA were determined.
(F) The nucleotide immediately following the canonical stop codon (G1) does not alter readthrough efficiency. ECs were transfected with VEGF-Ax-FLuc constructs containing G-to-C, G-to-A, and G-to-T substitutions. Relative FLuc activity and mRNA were measured.
See also Figure S3.