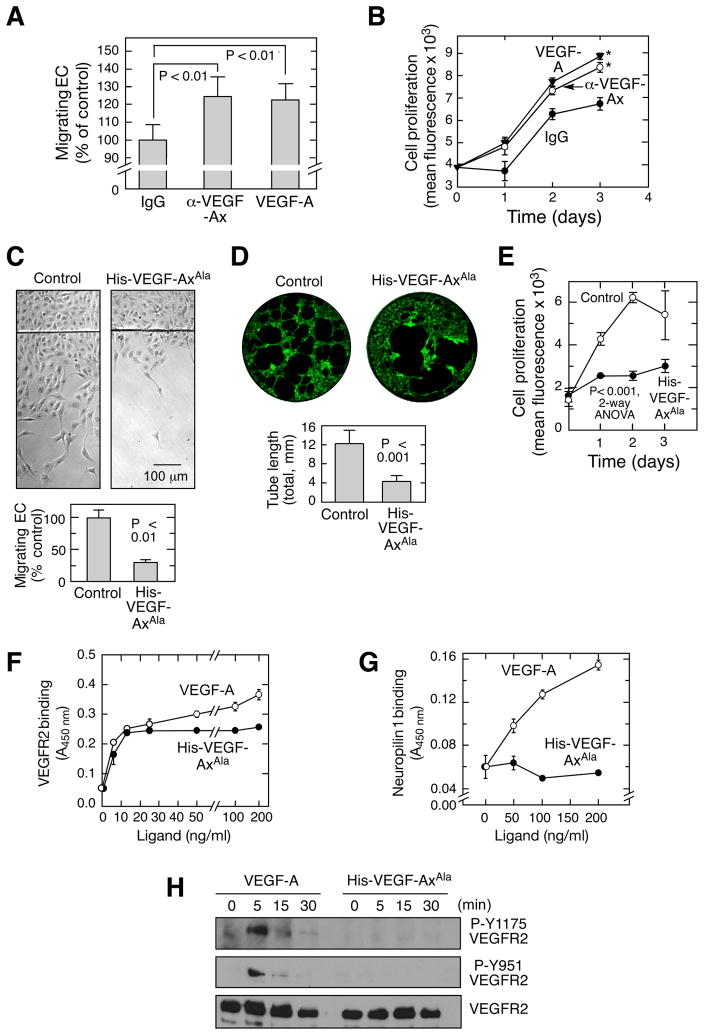
Figure 5. Anti-angiogenic properties of VEGF-Ax.
(A,B) Anti-VEGF-Ax antibody inhibits EC migration and proliferation. EC migration (A) in the presence of anti-VEGF-Ax antibody or recombinant human VEGF-A (20 ng/ml) was measured by razor-wound assay. Cell proliferation (B) was measured fluorimetrically as DNA (*, P < 0.05, 2-way ANOVA).
(C–E) Anti-angiogenic properties of VEGF-Ax. Migration (C), tube formation in Matrigel (D), and proliferation (E) of bovine ECs in the presence of recombinant His-VEGF-Axala (50 ng/ml).
(F–G) Binding of VEGF-A and His-VEGF-Axala to VEGFR2 (F) and neuropilin-1 (G). Binding was measured colorimetrically by solid phase enzyme-linked receptor-binding assay.
(H) Phosphorylation status of VEGFR2. HUVECs were treated with VEGF-A and His-VEGF-AxAla for up to 30 min and immunoblotted as shown.
See also Figure S4.