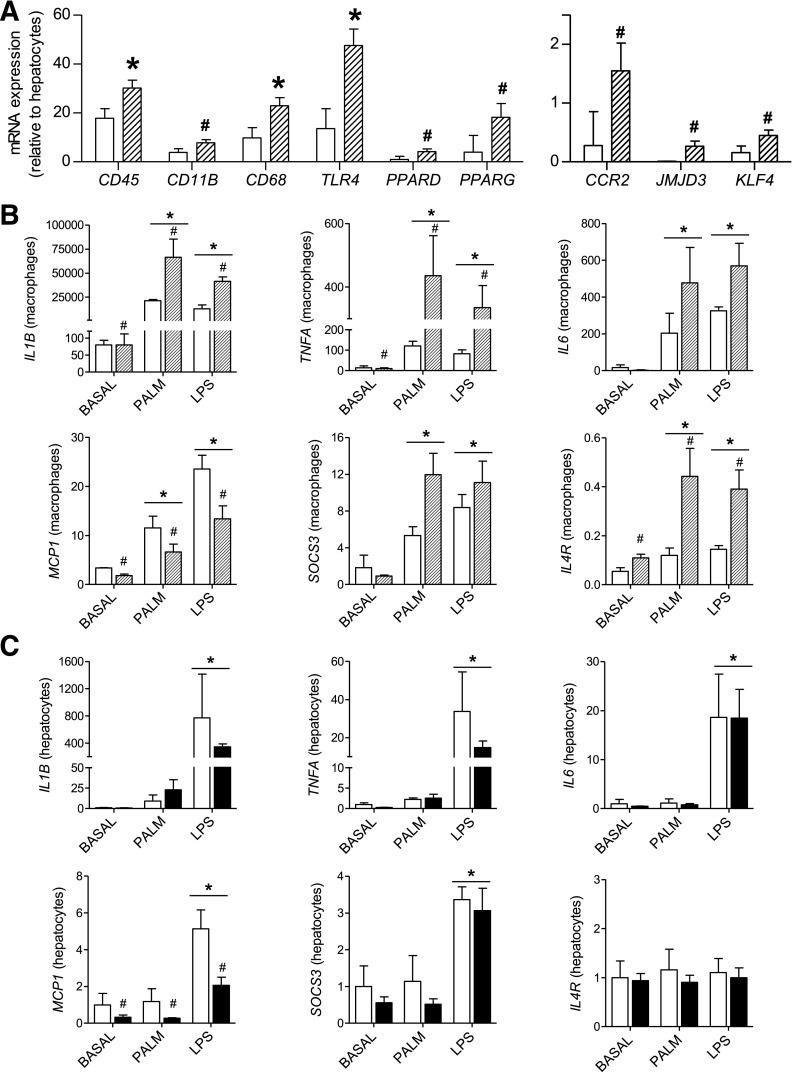
Figure 4.
Effect of maternal HF diet on hepatic macrophage and hepatocyte inflammatory activation. Hepatic macrophages and hepatocytes were isolated from juvenile livers and studied after 3 h of treatment with PALM and LPS compared with basal treatment (n = 2 CON/CON, 3 HF+IR/CON). A: Expression of canonical macrophage and activation markers in hepatic macrophages from CON/CON (white bars) and HF+IR/CON (dashed bars) offspring. Results shown are least square means and SEM for each offspring group. *P < 0.05 for main effect of offspring group; #P < 0.15. B: Expression of inflammatory genes in hepatic macrophages from CON/CON (white bars) and HF+IR (dashed bars) offspring following basal, LPS, and PALM treatment. C: Expression of inflammatory genes in hepatocytes from CON/CON (white bars) and HF+IR/CON (black bars) offspring following basal, LPS, and PALM treatment. In panels B and C, all results are expressed relative to hepatocyte basal CON/CON group. When the main effect of treatment was significant, comparisons between treatments are indicated: *P < 0.05 vs. BASAL. The main effect of maternal group (CON/CON versus HF+IR/CON) is shown as #P < 0.05.