Figure 6.
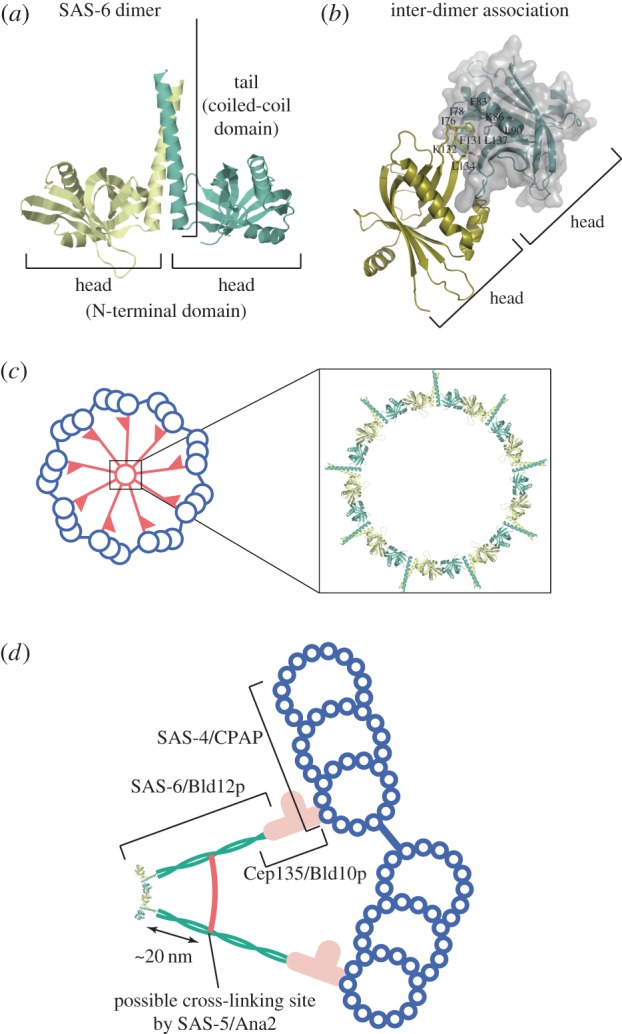
The three-dimensional structure of SAS-6 dimer and a model of SAS-6 assembly into the cartwheel [23,24]. (a) The structure of a zebrafish SAS-6 fragment that contains the N-terminal domain and part of the coiled-coil domain. The fragment forms a homodimer consisting of two globular heads and a coiled-coil tail. (b) The site of inter-dimer association in zebrafish SAS-6. The interaction is mostly between hydrophobic residues in the head domain. The hydrophobic Phe131 residue of one head is inserted into a hydrophobic pocket in the other head. Some of the residues that form the hydrophobic pocket are indicated. (c) SAS-6 ring model predicted by the structure. Nine SAS-6 dimers assemble into a ring with nine radiating filaments. This structure constitutes the central part of the cartwheel. (d) Localization of the cartwheel components. SAS-6/Bld12p constitutes the cartwheel hub and the central part of the spoke. Cep135/Bld10p constitutes the pinhead and a distal part of the spoke shaft and connects the cartwheel to the microtubules. Localizations of these proteins partially overlap. SAS-5/Ana2 may cross-link two cartwheel spokes at a site approximately 20 nm apart from the hub ring (see text). SAS-4/CPAP is localized around the microtubule. Localization of STIL, which binds to CPAP, is not established. (Online version in colour.)
