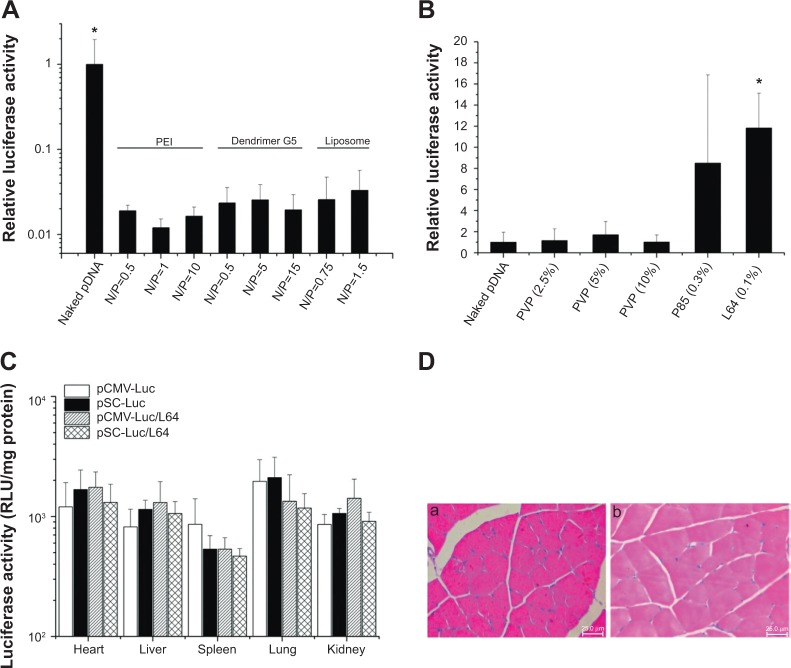
Figure 2.
Screening of materials for local gene delivery into skeletal muscle and the in vivo biocompatibility evaluation of pDNA/L64 combination.
Notes: (A and B) Screening of materials for local gene delivery into skeletal muscle. The bilateral tibialis anterior (TA) muscles were injected with 10 μg of naked pCMV-Luc or pCMV-Luc/material mixtures. Samples were obtained 7 days after injection. The luciferase activities in each group were measured and presented as the relative ratios compared with the naked pDNA group. (A) Cationic gene delivery materials (n=10). *P<0.05 versus all other groups. (B) Nonionic gene delivery materials (n=10). *P<0.05 versus naked DNA and the three PVP groups. (C and D) In vivo biocompatibility evaluation of pDNA/L64 combination. Ten micrograms of pCMV-Luc were injected into the left TA muscles of each mouse with or without 0.1% L64. The organs and muscles were detached 3 and 7 days after injection for detection. (C) Organ distribution of gene expression 3 days after intramuscular injection (n=6). (D) Representative tissue sections in the injected muscles 3 days after treatment: (a) pDNA, and (b) pDNA/L64 (n=6). Pluronic® L64 (Sigma-Aldrich, St Louis, MO, USA).
Abbreviations: pDNA, plasmid DNA; RLU, relative light units; CMV, cytomegalovirus; SV40E, SV40 enhancer; SC, CMV promoter/SV40 enhancer; Luc, luciferase; PVP, polyvinylpyrrolidone; PEI, polyethyleneimine; L64, Pluronic® L64; N/P, charge ratio between amino groups of materials and phosphate groups of DNA.