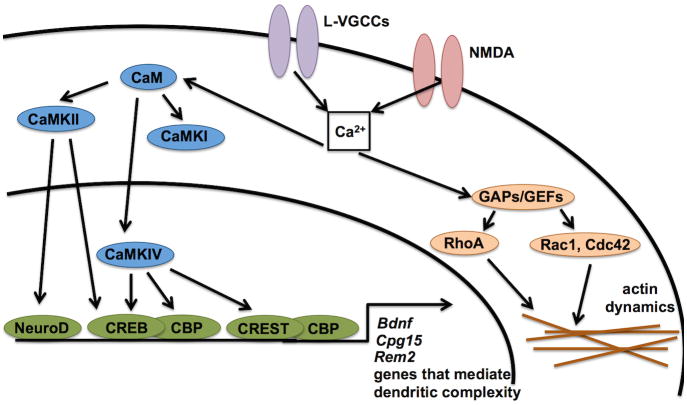
Figure 2.
Molecular signaling pathways that mediate activity-dependent changes in the dendritic arbor. Depolarization triggers calcium entry through multiple sources, including L-VGCCs and NMDA receptors. This leads to the activation of molecules (e.g. Rho GTPases) that directly interact with the cytoskeleton, as well as molecules (e.g. CaMKs) that regulate transcription factor activity that in turn causes changes in gene expression in the nucleus. Surprisingly little is known about the downstream targets of these pathways that mediate dendritic morphology.