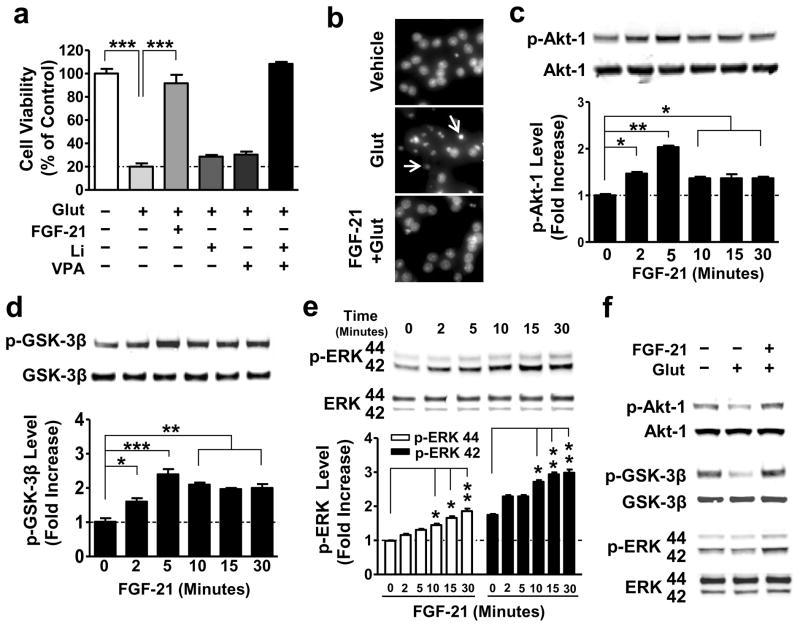
Figure 3. Exogenous FGF-21 protected against glutamate-induced neuronal death, and significantly increased phosphorylation of Akt-1, GSK-3β, and ERK 44/42.
(a) CGCs were pre-treated with 5 nM recombinant FGF-21 protein, 3 mM Li, 0.8 mM VPA, or a combination of Li with VPA for 6 days starting at DIV-6. At DIV-12, 100 μM glutamate was added to the culture and cell viability was determined 24 hours later by MTT assay. (b) CGCs treated with glutamate with or without FGF-21 pretreatment as described above were also examined for chromatin condensation using Hoechst 33258 staining. Arrows indicate neurons undergoing chromatin condensation. (c–e) CGCs were treated with 5 nM recombinant FGF-21 protein for the indicated times at DIV-6, then harvested, and processed for Western blotting to determine levels of p-Akt-1Ser473, p-GSK-3βSer9, and p-ERK 44/42Thr202/Tyr204. (f) CGCs were pre-treated with a combination of Li and VPA for 6 days starting at DIV-6, and then treated with glutamate for 6 hours, as described above. Cells were harvested for Western blotting to determine total and phosphorylated proteins of Akt-1Ser473, GSK-3βSer9, and ERK 44/42Thr202/Tyr204. Quantified data are means ± SEM and analyzed by one-way ANOVA, n=4; *P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001.