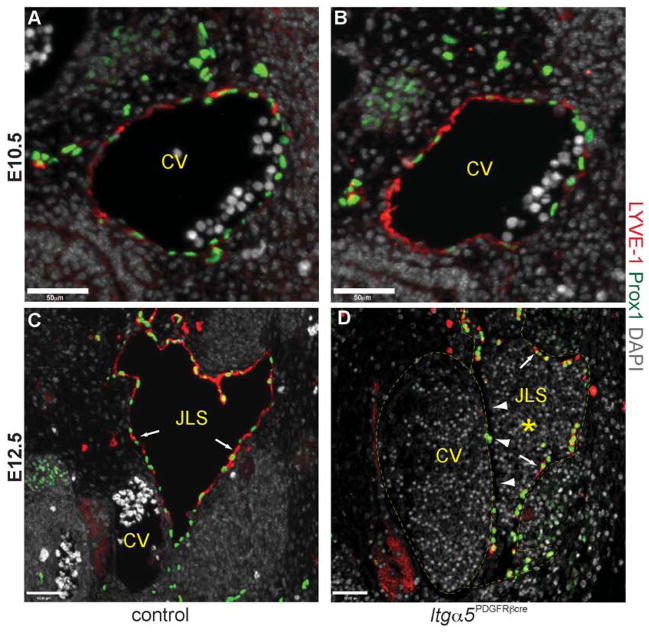
Figure 5. Separation of the jugular lymph sac from the cardinal vein is abnormal in Itg α5Pdgfrb-cre embryos.
Transverse sections through the cardinal vein (CV) showing expression of LYVE-1 (red) and Prox1 (green) in control and Itg α5Pdgfrb-cre embryos. At E10.5, equivalent numbers of Prox1+ lymphatic endothelial progenitor cells are expressed on the dorsal lateral side of the anterior cardinal vein in control (A) and Itg α5Pdgfrb-cre mice (B). Note that LYVE-1 is expressed throughout the CV at this stage.
These cells then bud, and migrate from the CV to form the jugular lymph sacs (JLS) by E12.5. In control embryos the JLSs now consist entirely of Prox1+ LYVE-1+ lymphatic endothelial cells (arrows, C) and contain no red blood cells. In contrast, JLSs in mutant embryos often contained blood (asterisk, D) and appeared to consist of both Prox1+ LYVE-1+ lymphatic endothelial cells (arrows, D), and Prox1+ Lyve1− and Prox1− Lyve-1− blood endothelial cells. This is most apparent directly adjacent to the CV (arrowheads, D). Scale bars: 50 μm.