Figure 2. Anatomical abnormalities of the Efnb2 CKO inner ear.
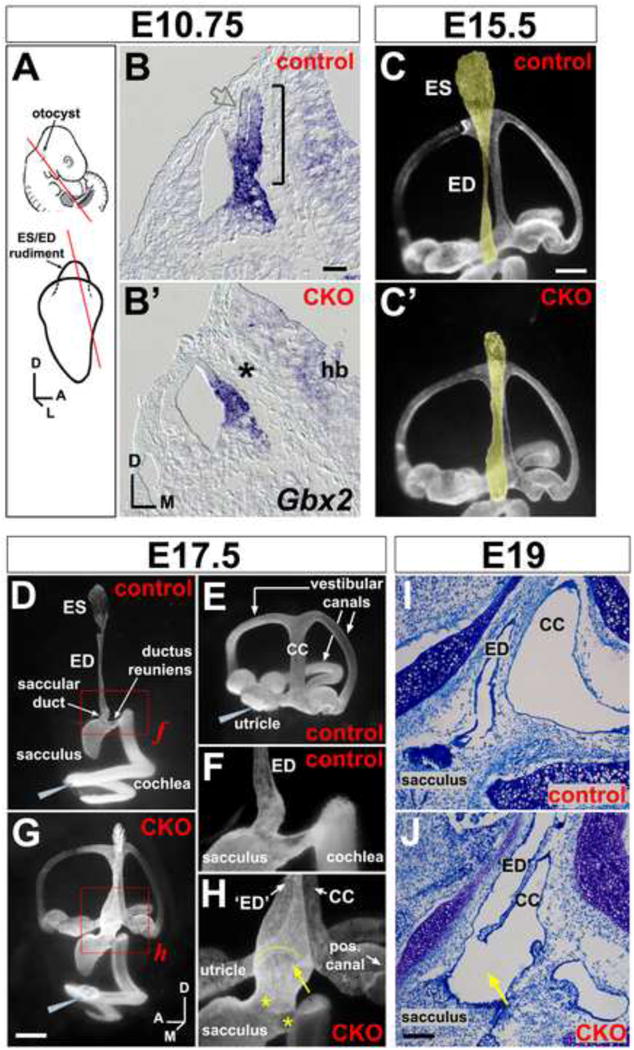
(A) Location of the otocyst at mid-gestation and projection of ES/ED rudiment from the dorso-medial otocyst. Lines show plane of section for (B,B′). (B,B′) E10.5 control (Efnbflox/+) and CKO littermates, hybridized for Gbx2 mRNA. Bracket in (B) highlights the endolymphatic projection; asterisk in (B′) highlights its absence; open grey arrow in (B) highlights weak Gbx2 signal at the endolymphatic epithelial lateral wall. Scale bar = 50 um; hb = hindbrain. (C,C′) Endolymph space of E15.5 control (Cre+;Efnb2flox/+) and CKO ears (medial views), visualized by paint injection. Endolymphatic epithelia are false-shaded yellow. Scale bar = 200 um. (D-H) Endolymph space of E17.5 control ears (Cre+;Efnb2flox/+; D,E), filled from either the cochlea (D) or utricle (E). Efnb2 CKO ear (G), filled with one injection to the cochlea. Grey wedges indicate injection site. (F and H) are magnified views of boxed regions in (D and G). Yellow arrow and arc in (H) highlight abnormal continuity across ED and common crus (CC). Asterisks in (H) highlight dysmorphic saccular duct and ductus reuniens. Scale bar in (G) = 400 microns in (D,E,G) and 150 microns in (F,H). Axes in (G) apply to (C-J). (I,J) Toluidine blue stained saggital sections through the head show abnormal luminal continuity (arrow in J) across endolymphatic epithelium (‘ED’) and common crus (CC) in an E19 Efnb2 CKO ear. (I) shows an Efnb2flox/+ control. Scale bar in (J) = 100 um and applies to (I,J).
