Figure 6. Failed proximal-distal (duct-sac) regionalization of the Efnb2 CKO endolymphatic epithelium.
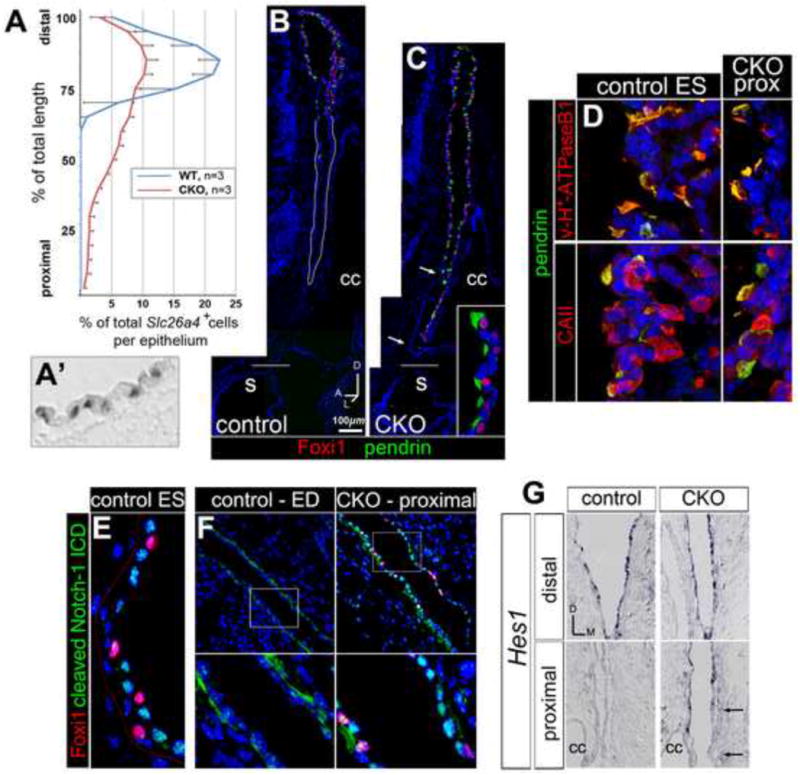
(A) Distributions of Slc26a4 mRNA signals along the proximal-distal length of endolymphatic epithelium for E19 Efnb2 CKO and control littermates. Error bars show standard deviation. (A′) Discrete Slc26a4 signals in a control epithelium. (B,C) Saggital sections through control (Efnb2+/flox, B) and Efnb2 CKO (C) E19 littermate heads, double immunolabeled for Foxi1 and pendrin. Distal/ES is toward the top. Horizontal lines mark level of insertion into the sacculus (s). Arrows in (C) highlight a proximal rostro-medial segment lacking ectopic signal. Inset in C shows proximal mutant cells (lumen is left). cc, common crus. (D) Control (Efnb2+/flox) and Efnb2 CKO E19 littermates, double immunolabeled for pendrin and either B1/B2 subunits of the vesicular proton pump or carbonic anhydrase II. CKO fields are of proximally (prox) located cells (lumen is left). (E,F) Control (Efnb2+/flox) and Efnb2 CKO E14.5 littermates, double immunolabeled for Foxi1 and cleaved Notch1-ICD. Lower panels in F show boxed regions in upper panels. Lower left panel in (F) highlights basal cytoplasmic Notch1-ICD signal in the control duct. (G) Transverse sections of control and CKO E14.5 littermates, hybridized for Hes1. Arrows highlight a proximal medial segment lacking ectopic signal. cc, common crus. Axes in (G) apply to (E-G).
