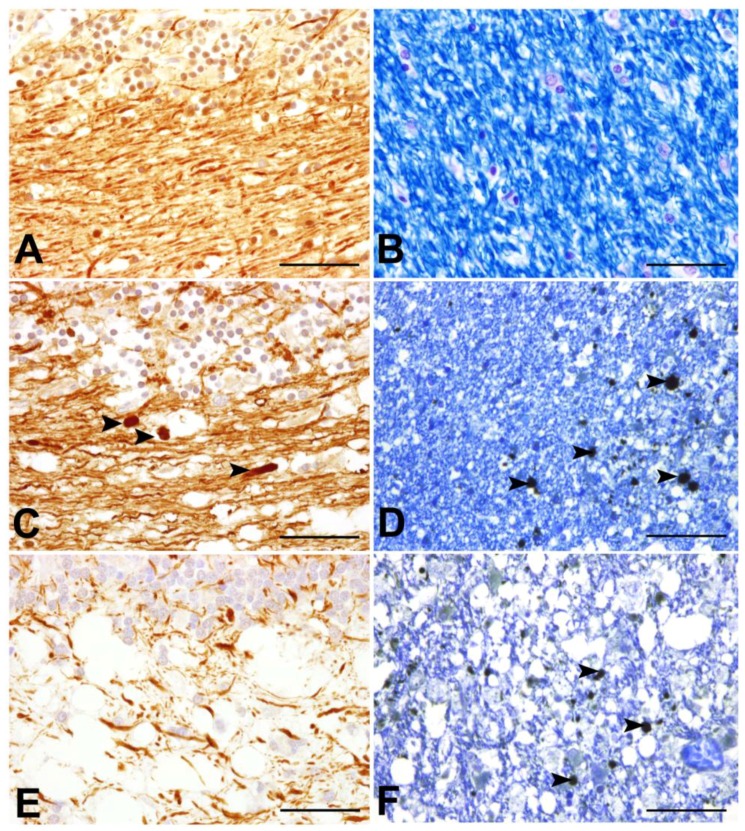
Figure 4.
Axonal pathology during the time course of CDV-DL. (A), (B) cerebellum of control dogs; (C),(D): acute lesions of canine distemper virus induced demyelinating leukoencephalitis (CDV-DL); (E),(F) subacute lesions of CDV-DL; (A),(C),(E) Immunohistochemical labelling of phosphorylated neurofilament (p-NF) in the cerebellar white matter; (B),(D),(F) Luxol Fast Blue staining for myelin in the cerebellar white matter; (D),(F) Double-labelling of myelin with LFB and immunohistochemical detection of beta amyloid precursor protein (β-APP). (A) Expression of p-NF in the cerebellar white matter of a control dog. Note the normal density of axons, which physiologically express p-NF; (B) LFB staining reveals normal myelin content in the cerebellar white matter of a control dog; (C) Expression of p-NF in the cerebellar white matter in an acute lesion of CDV-DL. The morphologically unremarkable axons stain positive for p-NF. Additionally, a slight decrease of the axonal density, represented by loss of p-NF-immunoreactivity is visible. Moreover, single swollen axonal structures also stain positive for p-NF (arrowheads), which might be attributed to accumulation of neurofilaments due to impaired axonal transport; (D) In an acute lesion of CDV-DL, staining with LFB demonstrates normal myelin density, while axonally transported β-APP is expressed by several swollen axons (arrowheads) in the cerebellar white matter. This observation is consistent with the inside-out theory based on the assumption of primary axonopathy; (E) Expression of p-NF in a subacute lesion of CDV-DL. A marked loss of p-NF-positive axonal structures (decreased axonal density) is evident; (F) Expression of β-APP in a subacute lesion of CDV-DL. As an expression of ongoing axonal damage, β-APP-immunoreactive axons (arrowheads) are present within demyelinated areas as demonstrated by reduced staining intensity for LFB. Bar = 50 µm. (A),(C),(D),(E),(F): Avidin-Biotin-Peroxidase Complex Method, 3.3’diaminobenzidine-tetrahydrochloride.