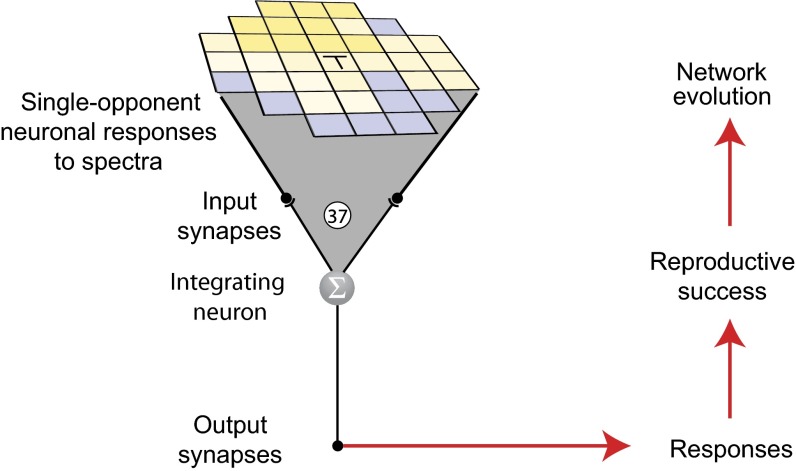
Fig. 2.
Neural network. The network input consisted of 37 blue-yellow single-opponent neurons that forwarded responses to natural stimuli to an integrating neuron (Σ) that then conveyed the summed values to an output synapse that, in biological vision, would provide input to higher order visual processing stations. The blue-yellow single-opponent neural responses approached 1 when the dominant input was yellowish (LM wavelengths) and 0 when the dominant input was bluish (S wavelengths). The criterion of reproductive success was approximation of the output values to the cumulative frequencies of occurrence of the central target spectrum (T), given the spectra of the surrounding elements in the pattern.