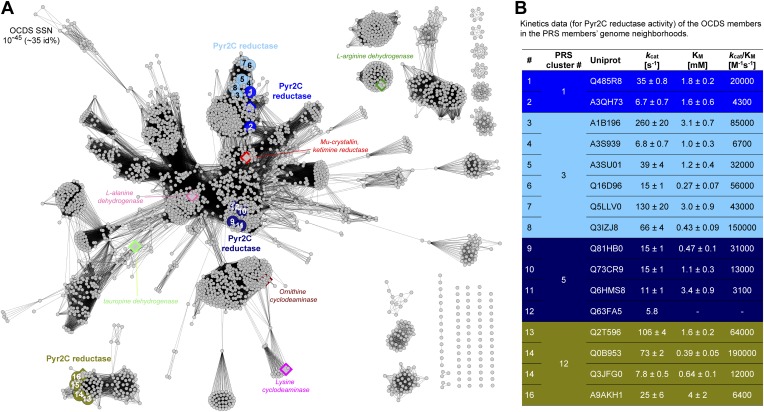
Figure 6. Sequence divergent members of the ornithine cyclodeaminase superfamily (OCDS) have been the assigned novel pyrroline-2-carboxylate reductase (Pyr2C reductase) function in this work.
(A) The OCDS SSN displayed at the e-value cutoff 10−45 (∼35% sequence identity). The Pyr2C reductase function is located in four clusters; these proteins are shown in large colored circles, labeled from 1 to 16, and color-coded by the colors of the PRS query sequences shown in Figure 2B. Proteins representing several previously characterized functions in the OCDS are shown by large diamonds, with borders in hotpink (L-alanine dehydrogenase [Schröder et al., 2004]), brown (ornithine cyclodeaminase [Goodman et al., 2004]), magenta (lysine cyclodeaminase [Gatto et al., 2006]), red (ketamine reductase [Hallen et al., 2011]), green (L-arginine dehydrogenase [Li and Lu, 2009]) and palegreen (tauropine dehydrogenase [Kan-No et al., 2005; Plese et al., 2008]), respectively. Their annotations are shown in italics. The diamonds with blue and olive borders are Pyr2C reductases recently characterized by Watanabe et al. (2014). (B) Kinetics data for the Pyr2C reductase activity for the 16 members of the OCDS shown in panel A using NADPH as the cosubstrate.