Figure 2.
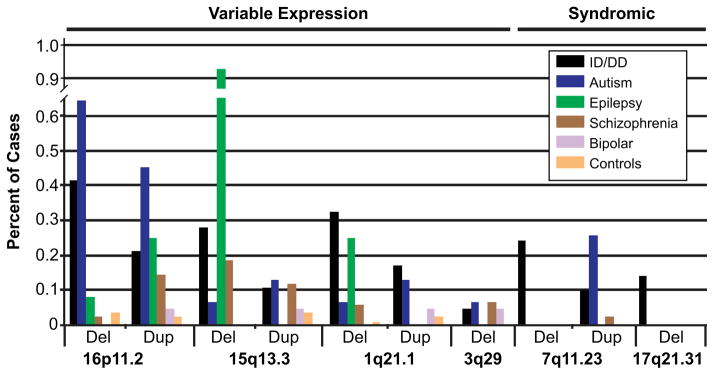
Variable expressivity of hotspot CNVs. The frequency of CNV deletions and reciprocal duplications for six genomic hotspots associated with neurological disease are shown (ID/DD, autism, epilepsy, schizophrenia, and bipolar disorders). Data sources are as follows. ID/DD: all sites n = 31,516 [Cooper et al., 2011; Kaminsky et al., 2011]. Autism: all sites n = 1,551 [Marshall et al., 2008; Sanders et al., 2011]. Epilepsy: all sites n = 399 [Mefford et al., 2010]; 15q13.3 n = 647 [Helbig et al., 2009; Mefford et al., 2010]; 16p11.2 n = 1,234 [de Kovel et al., 2010; Mefford et al., 2010]. Schizophrenia: all sites n = 4,168 [The International Schizophrenia Consortium, 2008; Malhotra et al., 2011], 15q13.3 n = 6,948 [The International Schizophrenia Consortium, 2008; Stefansson et al., 2008; Malhotra et al., 2011], 1q21.1 n = 12,117 [The International Schizophrenia Consortium, 2008; Stefansson et al., 2008; Malhotra et al., 2011], 3q29 n = 4,413 [The International Schizophrenia Consortium, 2008; Mulle et al., 2010; Malhotra et al., 2011]. Bipolar disorders: all sites n = 2,053 [Grozeva et al., 2010; Malhotra et al., 2011]. Controls: n = 8,329 [Cooper et al., 2011].
