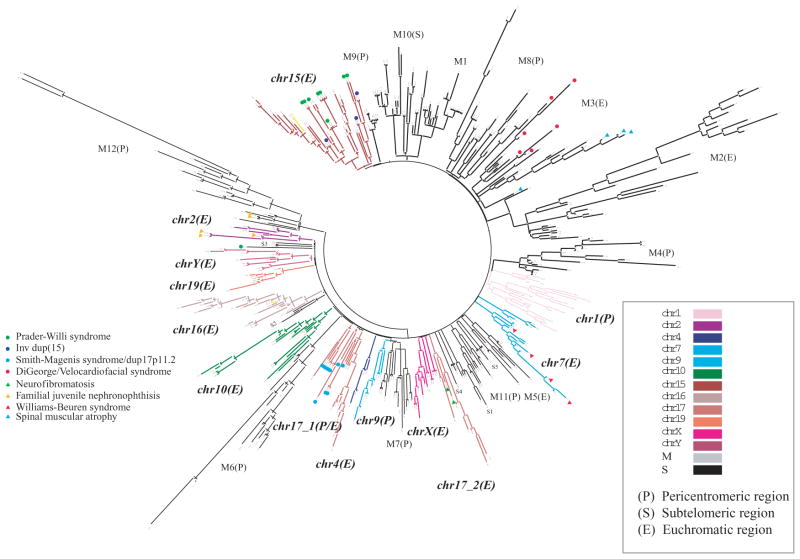
Figure 3.
Hierarchical clustering of human duplication blocks based on ancestral duplicon content. The termini of each branch represent one of 437 duplication blocks, which cluster into 24 distinct groups, 14 of which are restricted to a specific chromosome and 10 of which are mixed (M) among chromosomes mapping largely to subtelomeric (S) or pericentromeric (P) regions of the genome. An expanded view of chromosome 16 is shown (Fig. 5) (Jiang et al. 2007).