Figure 5.
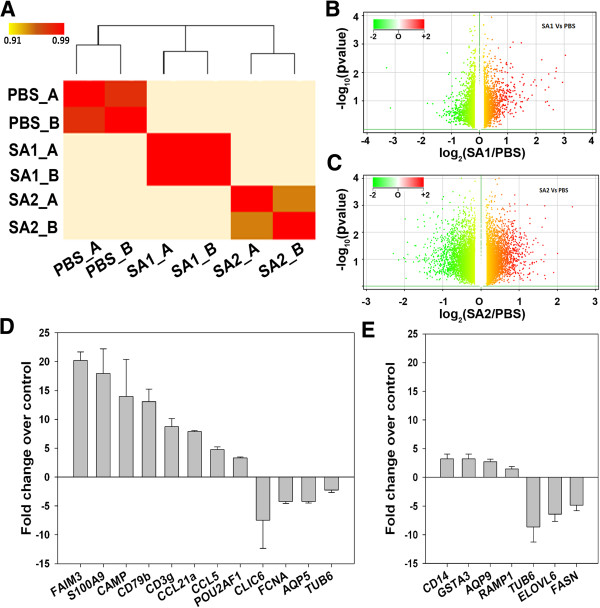
Staphylococcus aureus infection induces strain specific alteration of global gene expression in mice mammary tissue. (A) Expression heat map of sample-to-sample distances on the matrix of variance-stabilized data for overall gene expression. Darker red colors indicate more similar expression (color key is in arbitrary units). Clustering (top) demonstrates that the biological replicates of PBS, SA1 and SA2 samples are similar to each other but show complete separation among individual groups. (B) Differential gene expression, with fold difference between log2 normalized expression in SA1 inoculated (n = 2) and PBS inoculated mice mammary tissue (n = 2) plotted versus-log10 adjusted Pvalue. Each gene is colored on the basis of the log10 base mean expression. (C) Differential gene expression, with fold difference between log2 normalized expression in SA2 inoculated (n = 2) and PBS inoculated mice mammary tissue (n = 2) plotted versus-log10 adjusted P value. Each gene is colored on the basis of the log10 base mean expression. (D,E) Expression of a set of genes in the SA1 (D) or SA2 (E) infected mice mammary tissue was analyzed by qRT-PCR. The fold difference in expression of the genes in infected tissue over the PBS control tissue was calculated and plotted as the average of three biological replicates for SA1 and two biological replicates for SA2.
