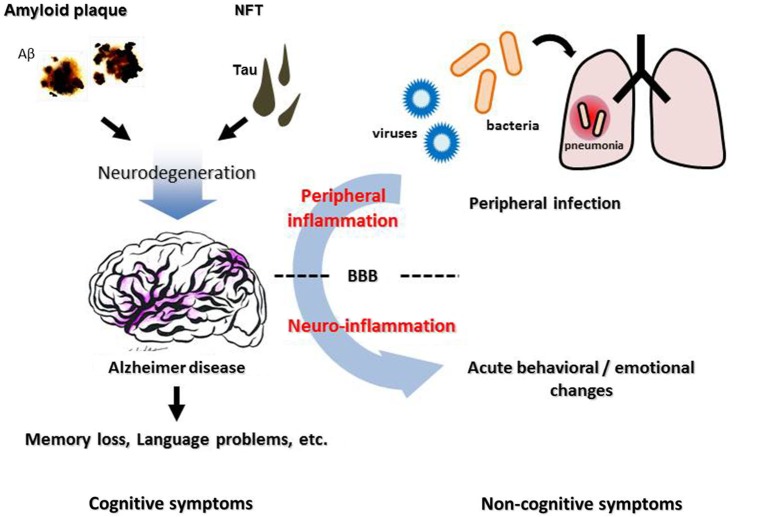
Figure 1.
Neuropathological features, inflammation, and cognitive/non-cognitive symptoms of Alzheimer disease. Cerebral accumulation of amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles (NFT) leads to neurodegeneration in the AD brain, which causes progressive cognitive dysfunction such as memory loss and language problems. Non-cognitive symptoms, such as agitation, aggression and psychosis, are often observed in AD patients, besides cognitive deterioration. These symptoms can be triggered by an infection in peripheral organs such as pneumonia, suggesting a contribution of peripheral inflammation. BBB, blood-brain barrier.