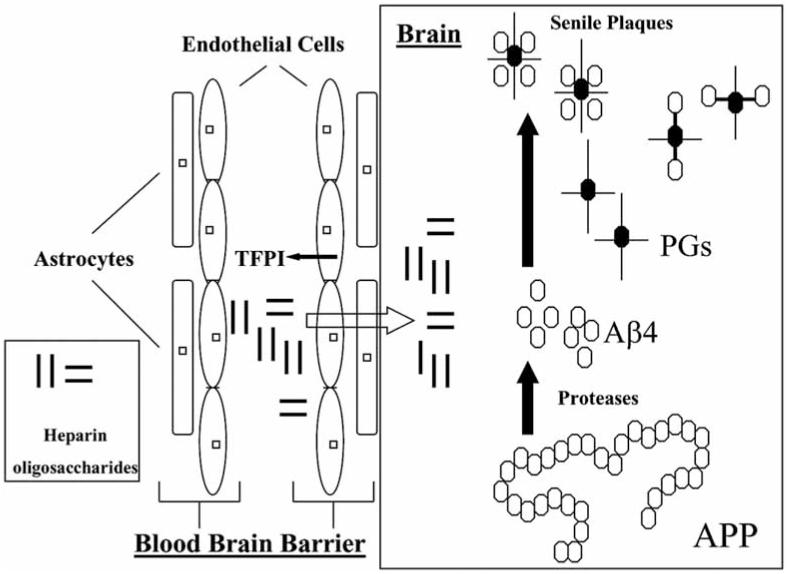
Fig. (2). Potential mechanisms of heparin oligosaccharides in the treatment and prevention of Alzheimer’s disease.
Heparin oligosaccharides may act at multiple sites. They are capable of releasing tissue factor pathway inhibitors (TFPI) from endothelial cell that exert anti-inflammatory and anti-atherosclerosis effects. After passing through the blood-brain barrier, they may interact with proteoglycans (PGs) to block the assembling of beta amyloid peptide (Aβ4) and PGs and senile plaque formation (APP: amyloid precursor protein).