Figure 2.
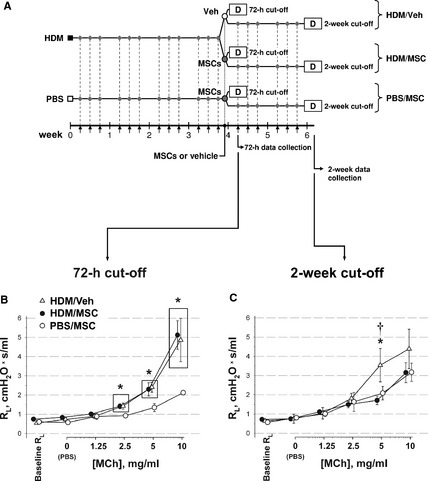
Study design and airway responsiveness to MCh. (A) Experimental asthma was induced in syngeneic mice by intranasal (i.n.) instillation of house dust mite (HDM) extract, three times weekly. Upon 4 weeks on instillations, the mice received 3 × 105 transduced mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) intravenously (i.v.) (HDM/MSC group). Control groups were HDM‐instilled mice receiving i.v. vehicle (HDM/Veh group), or phosphate‐buffered saline (PBS)‐instilled mice receiving MSCs (PBS/MSC group). Pulmonary mechanics and specimen harvesting were performed at 72 h after i.v. MSCs or vehicle (72‐h cutoff), or after 2 weeks of additional i.n. instillations (2‐week cutoff). For those animals studied on the 2‐week cutoff, i.n. installations were thus continued after MSC injection to represent a scenario where subjects undergo continuing exposure to an allergen regularly present in their environment. Small arrows in the time scale and corresponding diamonds indicate i.n. instillations; ‘D’, data collection points. (B, C) Pulmonary resistance (RL) upon MCh challenge was measured at the 72‐h (B) and 2‐week (C) cutoffs. *: P < 0.05 vs PBS/MSC; †: P < 0.05 vs HDM/MSC. The group symbol legend in (B) applies to (B, C).
