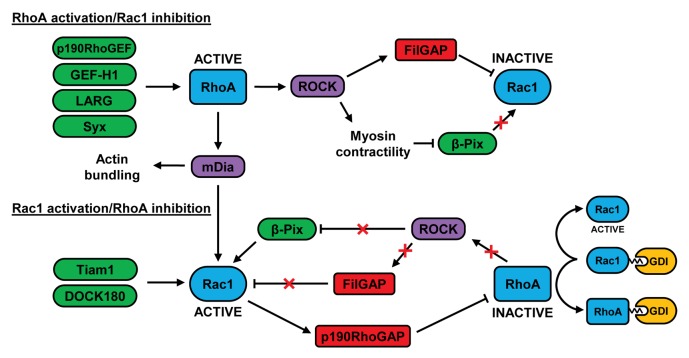
Figure 2. Crosstalk between RhoA and Rac1 in migrating cells. At the leading edge of migrating cells, RhoA can be activated by GEFs such as p190RhoGEF, GEF-H1, LARG, and Syx. At the cell rear, RhoA can restrict Rac1 activity via FilGAP and by negatively regulating the localization of β-Pix. RhoA-stimulated mDia activity may contribute to the subsequent increase in Rac1 activity at the leading edge, possibly by activating Src-dependent GEFs such as Tiam1 and DOCK180. Rac1 can inhibit RhoA via p190RhoGAP and the decrease in RhoA activity may further activate Rac1 by preventing FilGAP activation and by relieving the inhibition of β-Pix. The association of inactive RhoA with RhoGDI could also increase Rac1 activity as a result of the competitive binding of these 2 GTPases to GDI. See text for further details.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.