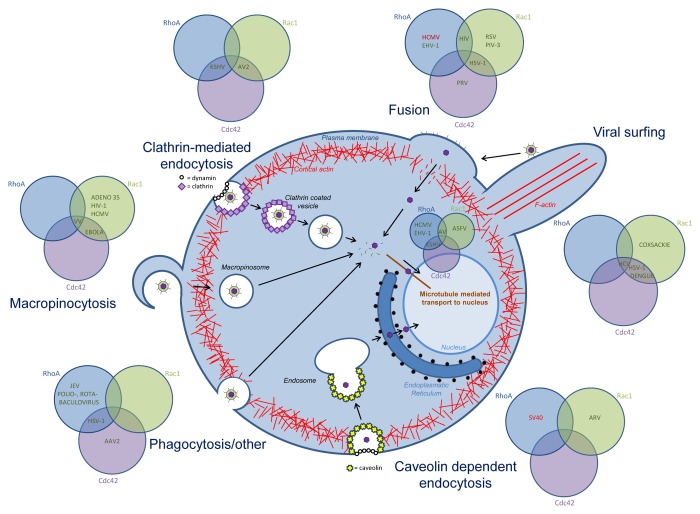
Figure 2. Overview of the role of Rho GTPase signaling in viral entry. Rho GTPases are involved in the different entry mechansims used by diverse viruses: membrane fusion, clathrin-mediated endocytosis, caveolin-dependent endocytosis, phagocytosis and other entry processes, and in viral transport to the nucleus. For each entry process, the involvement of Cdc42, Rac1 and/or RhoA is indicated, in green if the Rho GTPase is upregulated or activated, in red when the Rho GTPase is downregulated or inhibited. Abbreviations; Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV), adenovirus 2 (AV2), human cytomegalovirus (HCMV), equine herpesvirus (EHV-1), human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), parainfluenza virus 3 (PIV-3), herpes simplex virus (HSV-1), pseudorabies virus (PRV), hepatitis c virus (HCV), simian virus 40 (SV40), avian reovirus (ARV), Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV), adeno-associated virus 2 (AAV2), vaccinia virus (VV).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.