Abstract
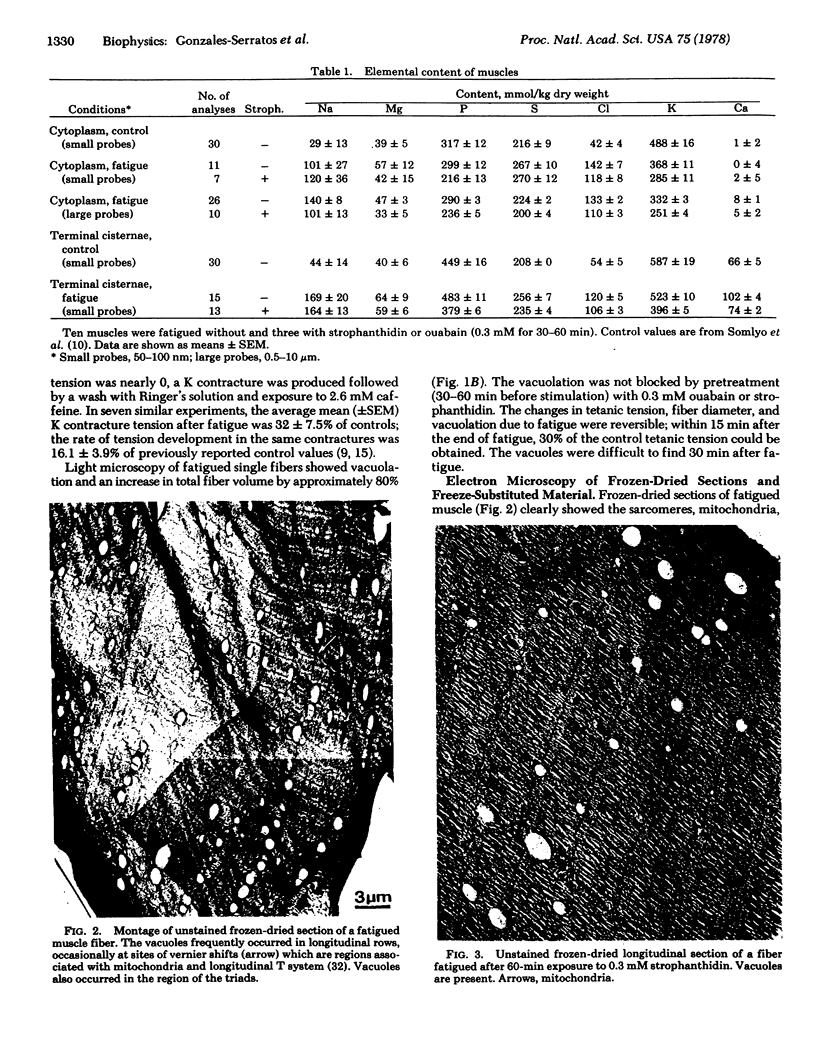
Electron probe analysis, cryo-ultramicrotomy, and freeze-substitution were used to determine the nature of vacuolation and the subcellular composition in fatigued frog skeletal muscle fibers. The vacuoles caused by fatigue were part of the T-tubule system and contained high concentrations of NaCl. The calcium concentration in the terminal cisternae was higher than previously measured normal resting values. Mitochondrial calcium content was relatively low (mean +/- SEM, 2 +/- 2 mmol/kg dry weight). Fiber NaCl was increased. It is concluded that fatigue is not due to the depletion of calcium stores from the terminal cisternae or to uncoupling of mitochondria due to calcium loading but may be caused by multiple mechanisms including failure of the T-tubule action potential.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birks R. I., Davey D. F. An analysis of volume changes in the T-tubes of frog skeletal muscle exposed to sucrose. J Physiol. 1972 Apr;222(1):95–111. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costantin L. L. The role of sodium current in the radial spread of contraction in frog muscle fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1970 Jun;55(6):703–715. doi: 10.1085/jgp.55.6.703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink R., Lüttgau H. C. An evaluation of the membrane constants and the potassium conductance in metabolically exhausted muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1976 Dec;263(2):215–238. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitts R. H., Holloszy J. O. Lactate and contractile force in frog muscle during development of fatigue and recovery. Am J Physiol. 1976 Aug;231(2):430–433. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1976.231.2.430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs F., Reddy Y., Briggs F. N. The interaction of cations with the calcium-binding site of troponin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Nov 17;221(2):407–409. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(70)90290-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis J. M. Les déplacements ioniques dans le muscles strié isolé après tétanisation répétée. Arch Int Physiol Biochim. 1964 Jan;72(1):124–153. doi: 10.3109/13813456409105258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis J. M. Les mouvements de l'eau dans le muscle strié isolé soumis à des tétanisations répétées. Arch Int Physiol Biochim. 1964 Jan;72(1):154–170. doi: 10.3109/13813456409105259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-serratos H. Graded activation of myofibrils and the effect of diameter on tension development during contractures in isolated skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1975 Dec;253(2):321–339. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grabowski W., Lobsiger E. A., Lüttgau H. C. The effect of repetitive stimulation at low frequencies upon the electrical and mechanical activity of single muscle fibres. Pflugers Arch. 1972;334(3):222–239. doi: 10.1007/BF00626225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HOROWICZ P. The effect of sudden changes in ionic concentrations on the membrane potential of single muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1960 Sep;153:370–385. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutter O. F., Warner A. E. Action of some foreign cations and anions on the chloride permeability of frog muscle. J Physiol. 1967 Apr;189(3):445–460. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutter O. F., Warner A. E. The pH sensitivity of the chloride conductance of frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1967 Apr;189(3):403–425. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krolenko S. A. Effect of fluxes of sugars and mineral ions on the light microscopic structure of frog fast muscle fibres. Nature. 1971 Feb 5;229(5284):424–426. doi: 10.1038/229424a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krolenko S. A. Vakuolizatsiia skeletnykh myshechnykh volokon. VI. Proiskhozhdenie vakuolei vo vremia vykhoda sakharov i mineral'nykh ionov. Tsitologiia. 1973 Oct;15(10):1244–1249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MASHIMA H., MATSUMURA M., NAKAYAMA Y. On the coupling relation between action potential and mechanical response during repetitive stimulation in frog sartorius muscle. Jpn J Physiol. 1962 Jun 15;12:324–336. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.12.324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamaru Y., Schwartz A. The influence of hydrogen ion concentration on calcium binding and release by skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Gen Physiol. 1972 Jan;59(1):22–32. doi: 10.1085/jgp.59.1.22. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuman H., Somlyo A. V., Somlyo A. P. Quantitative electron probe microanalysis of biological thin sections: methods and validity. Ultramicroscopy. 1976 Sep-Oct;1(4):317–339. doi: 10.1016/0304-3991(76)90049-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somlyo A. V., Shuman H., Somlyo A. P. Composition of sarcoplasmic reticulum in situ by electron probe X-ray microanalysis. Nature. 1977 Aug 11;268(5620):556–558. doi: 10.1038/268556a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somlyo A. V., Shuman H., Somlyo A. P. Elemental distribution in striated muscle and the effects of hypertonicity. Electron probe analysis of cryo sections. J Cell Biol. 1977 Sep;74(3):828–857. doi: 10.1083/jcb.74.3.828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VANHARREVELD A., CROWELL J. ELECTRON MICROSCOPY AFTER RAPID FREEZING ON A METAL SURFACE AND SUBSTITUTION FIXATION. Anat Rec. 1964 Jul;149:381–385. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091490307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vergara J. L., Rapoprot S. I., Nassar-Gentina V. Fatigue and posttetanic potentiation in single muscle fibers of the frog. Am J Physiol. 1977 May;232(5):C185–C190. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1977.232.5.C185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]









