Figure 1. Expression differences of 21 genes between patients with psychiatric events (PsAE) and without (NoPsAE), pre and post therapy.
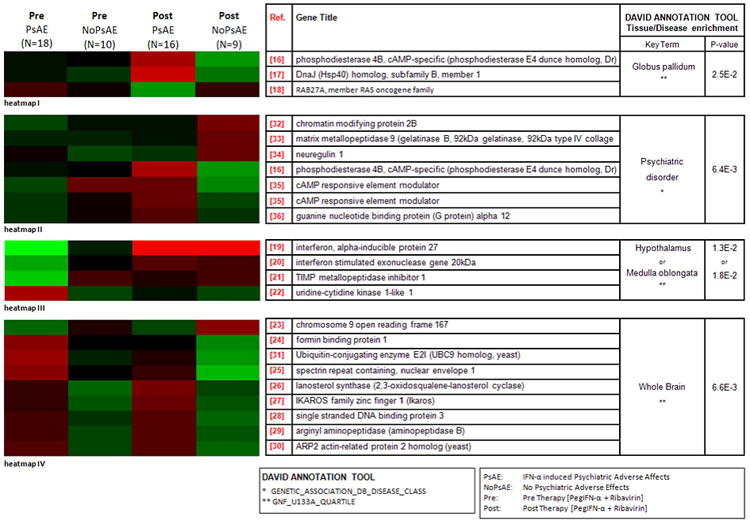
In patients (N=28) co-infected with the Human Immunodeficiency Virus/Hepatitis C Virus (HIV/HCV) DNA microarray analysis was performed using peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs). Serial overlapping of selected genes based on multi-contrast statistical and functional characterization algorithms led to identification of three gene subsets (heat map I-III) representing a panel of 12 unique molecular factors that reflect different biological states with respect to the development of Interferon-α (IFN-α) associated psychiatric adverse effects (PsAE). Furthermore, a 9-gene signature (heat map IV) characterized by sustained expression differences between eventful and uneventful patients pre and post therapy with pegylated Interferon-α and ribavirin (PegIFN-α/RBV) has been identified as containing genetic imprints associated likely with HIV and/or HCV related neurobehavioral disorders.
