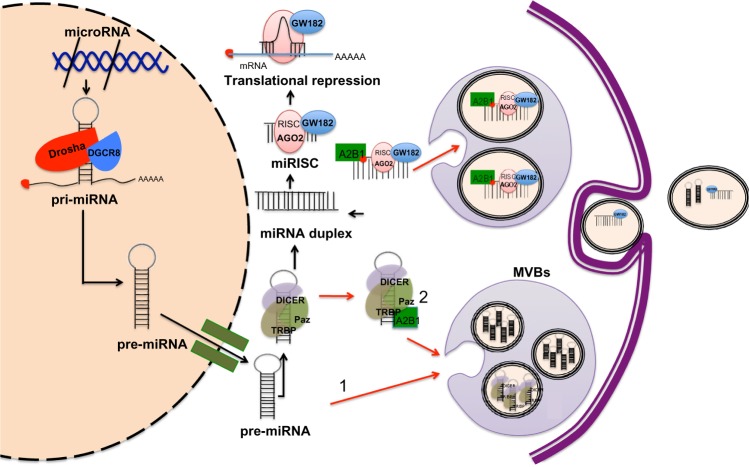
Figure 1.
Model of miRISC complex formation, incorporation into MVBs and subsequent secretion in exosomes.
Notes: (A) MiRNAs coding genes are transcribed as pri-miRNAs in the nucleus. Next, pri-miRNAs are processed by the microprocessor complex, which is composed by Drosha and DiGeorge syndrome critical region 8 to generate pre-miRNAs. Pre-miRNAs are exported to the cytoplasm by an anti-port transporter called exportin-5. Once in the cytoplasm, the pre-miRNAs are excised by Dicer to generate an intermediary RNA duplex ~22 nucleotides long. One strand of the RNA duplex is selected to be subsequently loaded into the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC) along with argonaut (AGO2) and GW182 to form mature RISC (miRISC) complex. MiRNAs in the miRISC can base pair with its target mRNA and induce translational repression and mRNA destabilization. If the miRISC does not interact with its target, it can then be selected and sorted into the MVBs, likely through a mechanism involving the protein hnRNPA2B1, which after being sumoylated, specifically binds miRNAs through the recognition of specific sequence motifs in the mature miRNA. Pre-miRNAs loaded into the RISC loading complex (pre-miRISC) may be sorted into MVBs (1). Sorting of pre-miRNAs into exosomes could also be occurring in a sequence-dependent manner (2); this, however, remains uncertain. Exosomes are derived from MVBs, also known as late endosomes. Exosomes containing miRISCs or pre-miRISCs are then secreted into the extracellular space. Black arrows indicate direction of canonic miRNA biogenesis and silencing action. Red arrows indicate direction of processes of miRNA maturation involving MVB production.
Abbreviations: hnRNPA2B1, heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A2B1; miRNA, microRNA; miRISC, miRNAs loaded into the RISC; mRNA, messenger RNA; MVB, multivesicular body; pre-miRNA, precursor miRNA; pri-miRNA, primary miRNA; RISC, RNA-induced silencing complex; TRPB, TAR RNA binding protein.