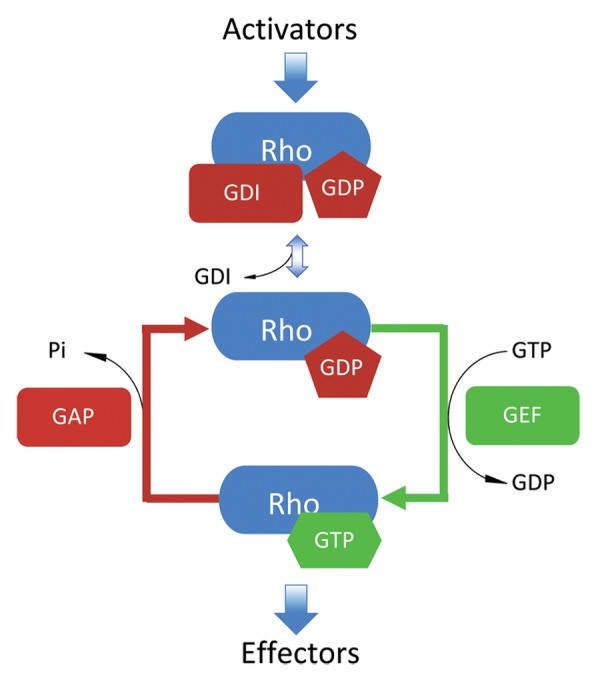
Figure 1. The GTPase cycle of Rho. Rho GTPases cycle between GTP-bound active states and GDP-bound inactive states. Guanine nucleotide dissociation inhibitors (RhoGDIs) extract lipid-modified Rho GTPases from cellular membranes to the cytosol and prevent GDP dissociation until released upon stimulus. Following signal input, the exchange of the bound GDP is facilitated by guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) that dramatically increase the dissociation rate of nucleotides. This promotes binding of GTP owing to its 10-fold higher in cellulo concentration vs. GDP. Once GTP-bound, active Rho is capable of binding downstream effectors and executing its biological functions. Rho remains active until GTP is converted to GDP due to its intrinsic hydrolytic capacity or through catalysis by GTPase activating proteins (GAPs).
