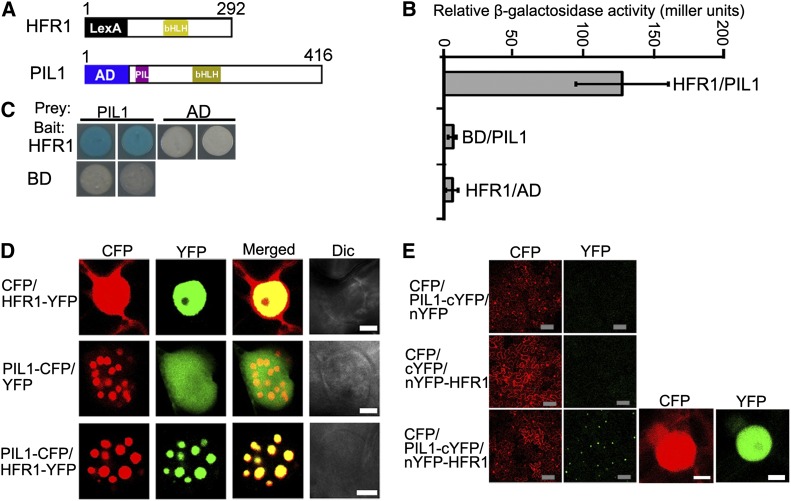
Figure 4.
PIL1 Physically Interacts with HFR1.
(A) Yeast two-hybrid bait construct of HFR1 fused to LexA DNA binding domain (LexA) and a prey construct of PIL1 fused to the B42 transcriptional activation domain (AD).
(B) Quantitative yeast two-hybrid assay showing the PIL1–HFR1 interaction. All vector combinations are given as bait/prey. Error bars represent ±sd (n = 10).
(C) Plate assays showing the PIL1–HFR1 interaction. The plates show the corresponding β-galactosidase activities represented by blue precipitates.
(D) PIL1 and HFR1 localize together to NBs in tobacco cells. Dic, differential interference contrast. Bars = 5 μm.
(E) BiFC assay of the PIL1–HFR1 interaction in tobacco leaf cells. CFP serves as the internal control. The left two panels show the wide field view to indicate the BiFC efficiency. The right two panels show a single nucleus at high magnification. Gray bars = 100 μm; white bars = 5 μm.