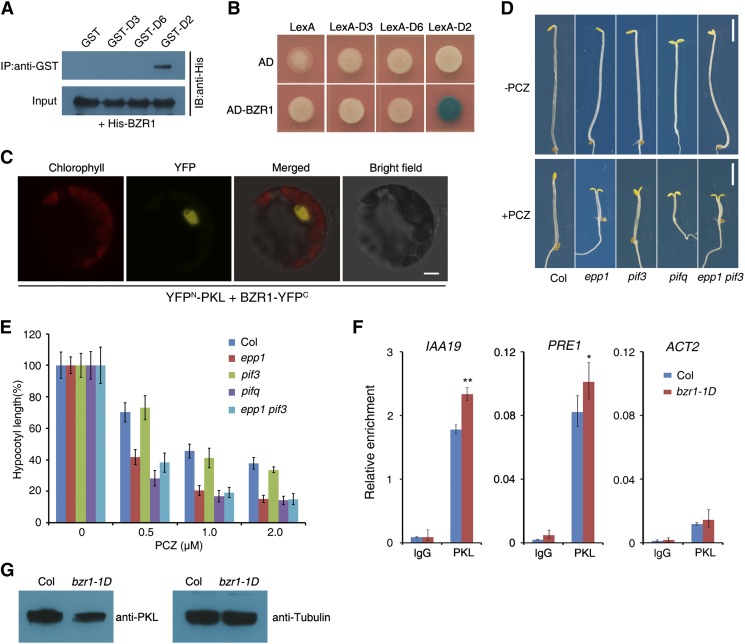
Figure 4.
PKL Interacts with BZR1.
(A) In vitro pull-down assay between recombinant His-BZR1 and various PKL fragments tagged with GST. His-BZR1 proteins were incubated with immobilized GST or GST-PKL, and immunoprecipitated fractions were probed with an anti-His antibody. IB, immunoblot; IP, immunoprecipitation.
(B) Yeast two-hybrid assay between BZR1 fused with the B42 activation domain (AD) and the D2, D3, or D6 fragment of PKL (Supplemental Figure 1A) fused with the LexA DNA binding domain.
(C) BiFC assay showing that YFPN-PKL and BZR1-YFPC interact to form a functional YFP in the nucleus of Arabidopsis protoplasts. Chlorophyll, chlorophyll autofluorescence; YFP, YFP fluorescence; merged, chlorophyll and YFP fluorescence. Bar = 5 μm.
(D) Effect of BR biosynthesis inhibition on seedling growth. The panels show phenotypes of Col wild-type, epp1, pif3, and epp1 pif3 seedlings grown in medium with or without 1 μM of the BR biosynthesis inhibitor PCZ in darkness for 5 d. Bars = 2 mm.
(E) Relative hypocotyl lengths of seedlings grown in various concentrations of PCZ for 5 d. Data represent means ± sd of at least 20 seedlings.
(F) ChIP-qPCR assay showing the relative enrichment of IAA19, PRE1, and ACT2 (negative control) genomic fragments upon precipitation with an anti-PKL antibody. Col and bzr1-1D seedlings were grown in darkness for 5 d. Data represent means ± sd of three biological replicates. Asterisks indicate significant differences from the wild type at P < 0.05 (*) or P < 0.01 (**) using Student’s t test.
(G) Immunoblot assay for PKL in the bzr1-1D mutant. Immunoblotting against tubulin antibody served as the loading control.