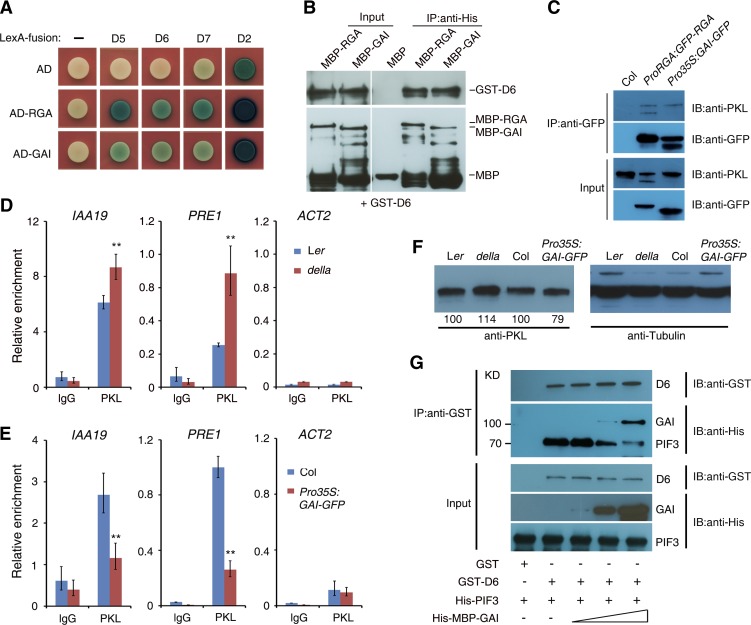
Figure 5.
RGA and GAI Interact with PKL and Inhibit Its Binding Activity.
(A) Yeast two-hybrid analysis of either RGA or GAI fused to the B42 activation domain (AD) and different fragments of PKL (Supplemental Figure 1A) fused to LexA-BD.
(B) In vitro pull-down assay. Recombinant proteins of GST-D6 and MBP-RGA or MBP-GAI (input; left panels) were immunoprecipitated with an anti-His antibody and then immunoblotted using either anti-GST (top right panel) or anti-MBP (bottom right panel). IB, immunoblot; IP, immunoprecipitation.
(C) Co-IP assay between PKL and RGA or GAI. Col wild-type, ProRGA:RGA-GFP, and Pro35S:GAI-GFP seedlings were grown in darkness for 5 d. Total protein extracts (input; bottom panels) were immunoprecipitated with an anti-GFP antibody (top panels) and then immunoblotted using either anti-GFP or anti-PKL antibody.
(D) and (E) ChIP-qPCR assay showing the relative enrichment of IAA19, PRE1, and ACT2 (negative control) promoter fragments upon precipitation with anti-PKL antibody in the della mutant (D) or the Pro35S:GAI-GFP transgenic line (E). Seedlings were grown in darkness for 5 d. Data represent means ± sd of biological triplicates. Asterisks indicate significant differences from the wild type at P < 0.01 using Student’s t test. Ler, Landsberg erecta.
(F) Immunoblot assay showing PKL protein levels in the della mutant and GAI overexpression plants and their corresponding wild types. Immunoblotting against tubulin antibody served as the loading control. Values denote relative amounts of PKL normalized to the tubulin control, and values in the wild type are set as 100.
(G) Pull-down assay showing that GAI blocks the PKL–PIF3 interaction. Recombinant protein GST-D6 was preincubated with His-MBP-GAI for 1 h. His-PIF3 was then added and incubated for an additional 1 h. It should be noted that the GST band was not shown due to its low molecular mass.