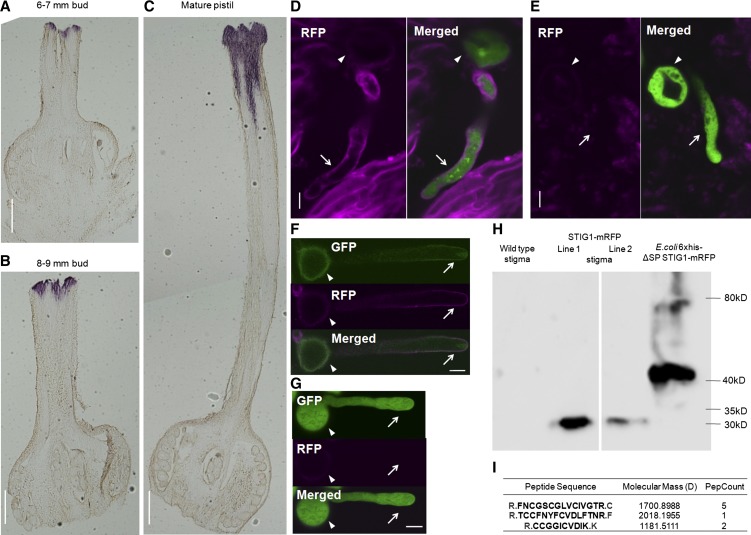
Figure 1.
Tomato STIG1 Transcript Is Present in Mature Stigmas and STIG1 Is Processed in Stigmatic Exudate.
(A) to (C) In situ hybridization of STIG1 mRNA in a 6- to 7-mm flower bud (A), an 8- to 9-mm flower bud (B), and a mature pistil (C). Bars = 1 mm.
(D) and (E) Confocal images of eGFP-expressing pollen germinating in the stigma of a pistil expressing STIG1-mRFP (D) or a wild-type pistil (E).
(F) A representative ProLePRK2:LePRK2-eGFP pollen grain that had germinated on a transgenic tomato pistil expressing STIG1-mRFP for 1 h and then was washed from the stigma using germination medium.
(G) A representative eGFP-expressing pollen tube flushed from a wild-type stigma.
For (F) and (G), arrows and arrowheads indicate pollen tubes and pollen grains, respectively. Bars = 10 μm.
(H) Immunoblot analysis with anti-mRFP monoclonal antibody detects a 32-kD fusion protein in transgenic plants expressing STIG1-mRFP.
(I) STIG1 peptides in the 5- to 10-kD section of proteins from tomato stigma exudate, identified by ESI-MS. Trypsin digestion sites are shown in gray. PepCount indicates the number of matching peptides identified in ESI-MS.