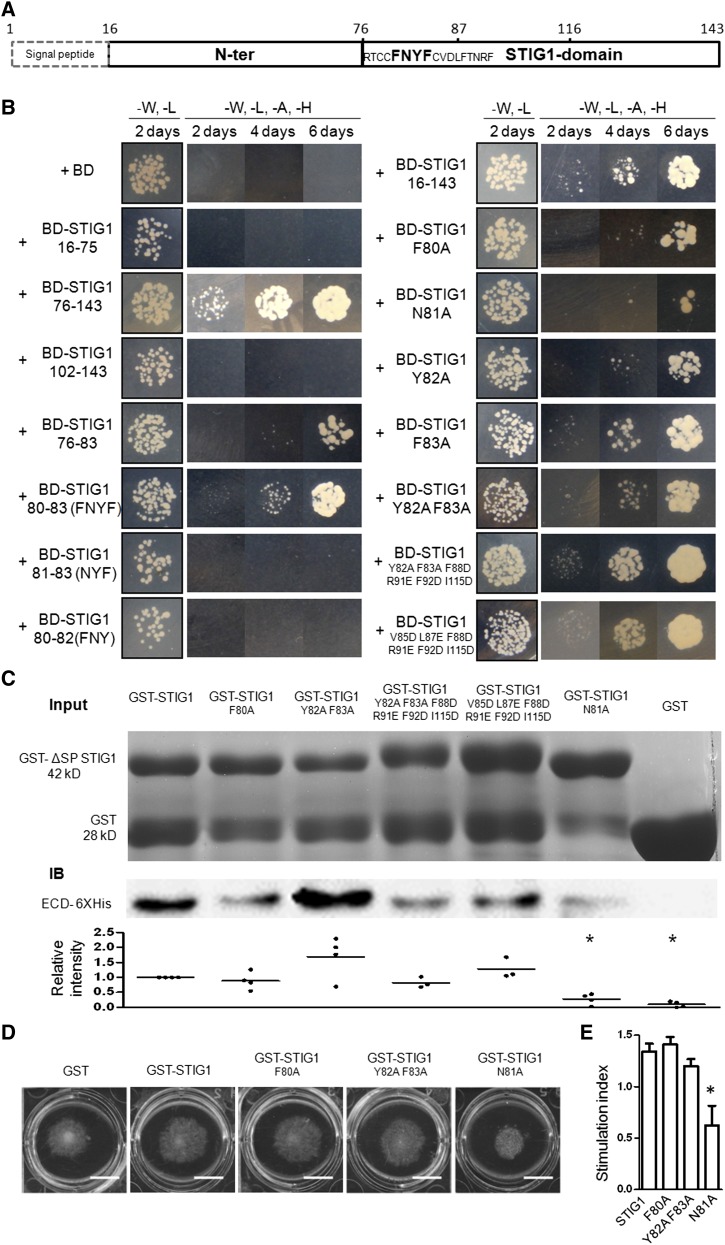
Figure 4.
Amino Acids F80N81Y82F83 in the Cys-Rich STIG1 Domain Are Necessary and Sufficient for Interaction with the Extracellular Domain of LePRK2.
(A) Schematic diagram of functional motifs/sites in STIG1. Numbers indicate amino acid positions. The FNYF motif is shown in boldface.
(B) Growth of yeast cells cotransformed with pGADT7-ECD2 and the listed constructs. Transformants were spotted on SD/-Leu-Trp or SD/-Leu-Trp-His-Ade medium.
(C) GST pull-down assay. Top panel, SDS-PAGE analysis of GST or GST fusion proteins. One-fifth of the corresponding proteins were loaded as an input control. Middle panel, proteins bound to Glutathione Sepharose 4B were separated by SDS-PAGE and detected with an anti-His monoclonal antibody. A representative gel is shown. Bottom panel, relative intensities in at least three experiments.
(D) Pollen tube growth promotion assay with wild-type or mutated GST-ΔSP STIG1. Bars = 1 cm.
(E) Pollen tube growth promotive effect of STIG1 and its mutants. Equal amounts of recombinant protein (250 nM each) were used. Error bars indicate se. n = 3 independent experiments. The asterisk indicates a significant difference from wild-type STIG1 (P < 0.05, Student’s t test).