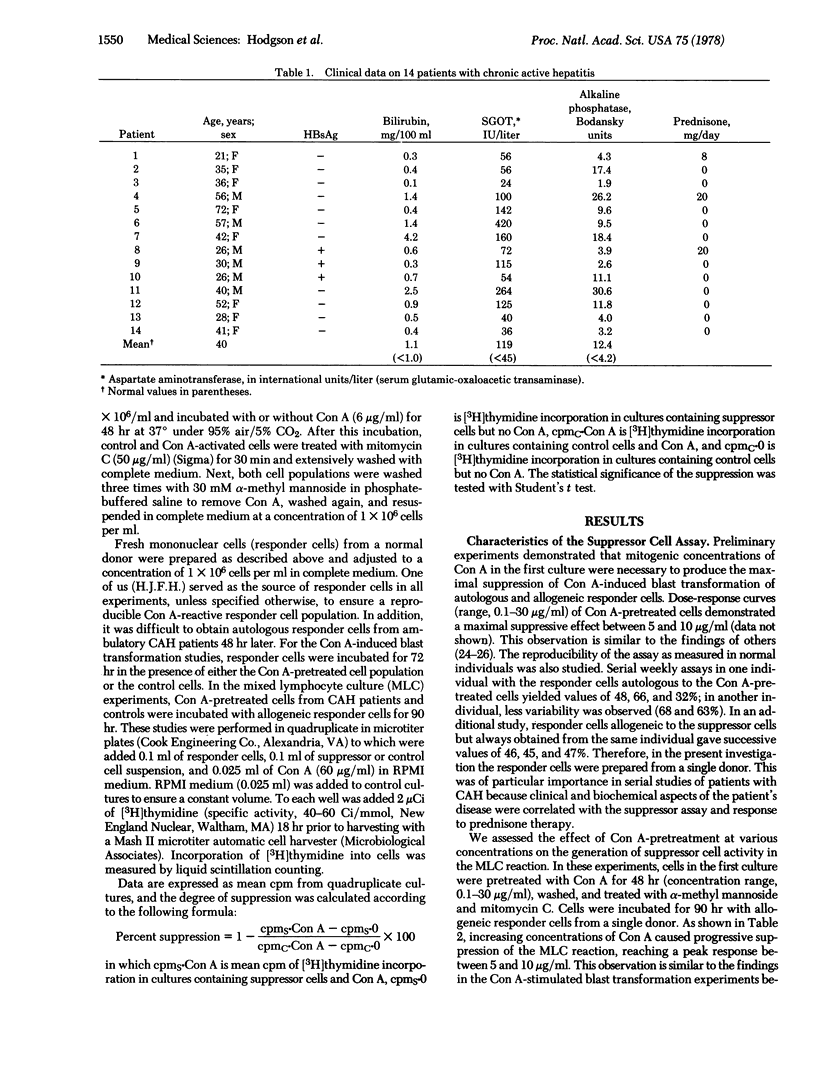
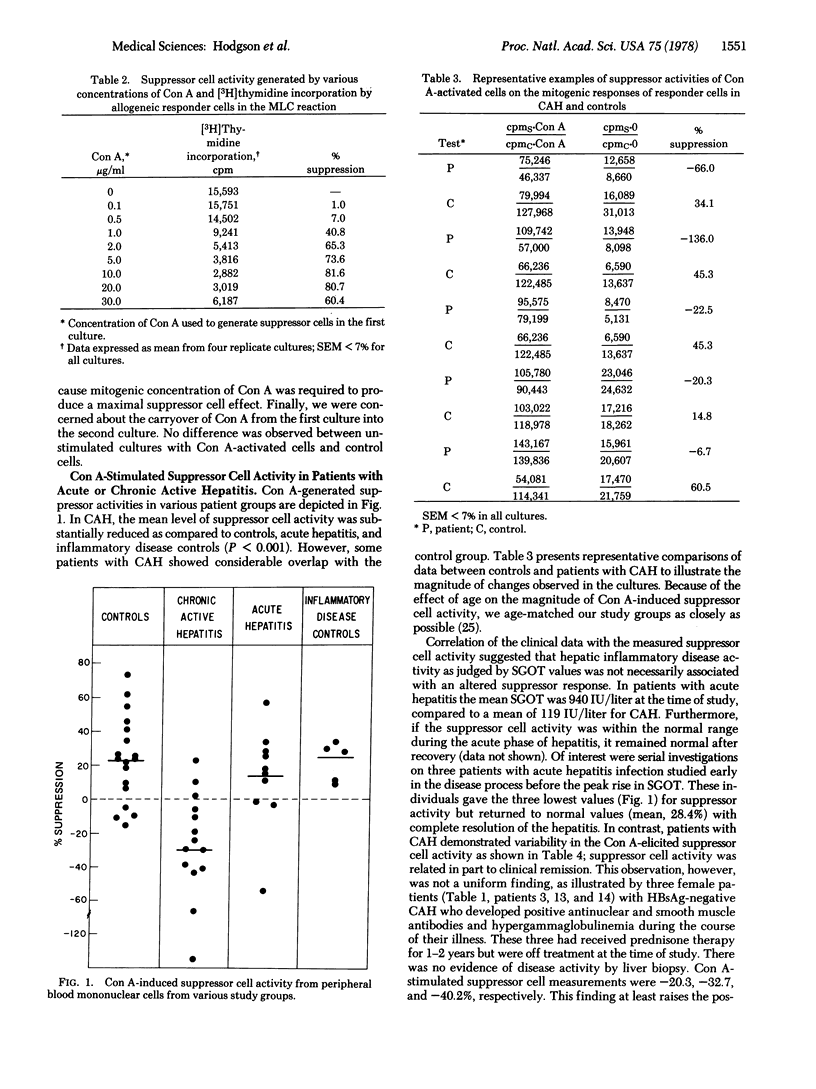
Abstract
We have studied peripheral blood mononuclear cells obtained from 24 patients with acute or chronic active hepatitis to determine if there was an abnormality in concanavalin A-induced suppressor cell activity compared to control subjects. Suppressor cells were generated by preincubation of the mononuclear cells with a mitogenic concentration of concanavalin A (6 μg/ml) for 48 hr followed by treatment with mitomycin C and α-methyl mannoside. Suppressor cell activity was assessed in second cultures by inhibition of concanavalin A-stimulated blast transformation of fresh allogeneic lymphocytes. Concanavalin A-stimulated suppressor activity was not elicited in mononuclear cells from the majority of patients with chronic active hepatitis in contrast to patients with acute hepatitis or acute inflammatory diseases and controls (P < 0.001). This finding was demonstrable in chronic active hepatitis patients in remission and relapse, both on and off prednisone therapy, and varied considerably during the course of the disease. The extent of liver injury was not related to the measured suppressor cell activity. These studies suggest that in chronic active hepatitis, a disease in which the host immune response may be involved, there appears to be a defect in concanavalin A-stimulated suppressor cells.
Keywords: concanavalin A, lymphocytes, prednisone, cell culture
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abdou N. I., Sagawa A., Pascual E., Hebert J., Sadeghee S. Suppressor T-cell abnormality in idiopathic systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1976 Sep;6(2):192–199. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(76)90110-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bresnihan B., Jasin H. E. Suppressor function of peripheral blood mononuclear cells in normal individuals and in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest. 1977 Jan;59(1):106–116. doi: 10.1172/JCI108607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broder S., Humphrey R., Durm M., Blackman M., Meade B., Goldman C., Strober W., Waldmann T. Impaired synthesis of polyclonal (non-paraprotein) immunoglobulins by circulating lymphocytes from patients with multiple myeloma Role of suppressor cells. N Engl J Med. 1975 Oct 30;293(18):887–892. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197510302931801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantor H., Shen F. W., Boyse E. A. Separation of helper T cells from suppressor T cells expressing different Ly components. II. Activation by antigen: after immunization, antigen-specific suppressor and helper activities are mediated by distinct T-cell subclasses. J Exp Med. 1976 Jun 1;143(6):1391–1340. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.6.1391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham A. J. Self-tolerance maintained by active suppressor mechanisms. Transplant Rev. 1976;31:23–43. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1976.tb01451.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeHoratius R. J., Strickland R. G., Williams R. C., Jr T and B lymphocytes in acute and chronic hepatitis. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1974 Apr;2(3):353–360. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(74)90053-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutton R. W. Inhibitory and stimulatory effects of concanavalin A on the response of mouse spleen cell suspensions to antigen. I. Characterization of the inhibitory cell activity. J Exp Med. 1972 Dec 1;136(6):1445–1460. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.6.1445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutton R. W. Suppressor T cells. Transplant Rev. 1975;26:39–55. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1975.tb00174.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folch H., Waksman B. H. The splenic suppressor cell. II. Suppression of mixed lymphocyte reaction by thymus-dependent adherent cells. J Immunol. 1974 Jul;113(1):140–144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershon R. K., Kondo K. Antigenic competition between heterologous erythrocytes. I. Thymic dependency. J Immunol. 1971 Jun;106(6):1524–1531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershon R. K., Kondo K. Cell interactions in the induction of tolerance: the role of thymic lymphocytes. Immunology. 1970 May;18(5):723–737. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallgren H. M., Yunis E. J. Suppressor lymphocytes in young and aged humans. J Immunol. 1977 Jun;118(6):2004–2008. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubert C., Delespesse G., Govaerts A. Concanavalin A-activated suppressor cells in normal human peripheral blood lymphocytes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Oct;26(1):95–98. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jandinski J., Cantor H., Tadakuma T., Peavy D. L., Pierce C. W. Separation of helper T cells from suppressor T cells expressing different Ly components. I. Polyclonal activation: suppressor and helper activities are inherent properties of distinct T-cell subclasses. J Exp Med. 1976 Jun 1;143(6):1382–1390. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.6.1382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackay I. R., Morris P. J. Association of autoimmune active chronic hepatitis with HL-A1,8. Lancet. 1972 Oct 14;2(7781):793–795. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)92149-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadler L. M., Hodes R. J. Regulatory mechanisms in cell-mediated immune responses. II. Comparison of culture-induced and alloantigen-induced suppressor cells in MLR and CML. J Immunol. 1977 May;118(5):1886–1895. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul W. E., Benacerraf B. Functional specificity of thymus- dependent lymphocytes. Science. 1977 Mar 25;195(4284):1293–1300. doi: 10.1126/science.320663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peavy D. L., Pierce C. W. Cell-mediated immune responses in vitro. I. Suppression of the generation of cytotoxic lymphocytes by concanavalin A and concanavalin A-activated spleen cells. J Exp Med. 1974 Aug 1;140(2):356–369. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.2.356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich R. R., Rich S. S. Biological expressions of lymphocyte activation. IV. Concanavalin A-activated suppressor cells in mouse mixed lymphocyte reactions. J Immunol. 1975 Mar;114(3):1112–1115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakane T., Green I. Human suppressor T cells induced by concanavalin A: suppressor T cells belong to distinctive T cell subclasses. J Immunol. 1977 Sep;119(3):1169–1178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sampson D., Grotelueschen C., Kauffman H. M., Jr The human splenic suppressor cell. Transplantation. 1975 Nov;20(5):362–367. doi: 10.1097/00007890-197511000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sampson D., Kauffman H. M., Jr, Grotelueschen C., Metzig J. Suppressor activity of the human spleen and thymus. Surgery. 1976 Apr;79(4):393–397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shou L., Schwartz S. A., Good R. A. Suppressor cell activity after concanavalin A treatment of lymphocytes from normal donors. J Exp Med. 1976 May 1;143(5):1100–1110. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.5.1100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinclair N. R., Lees R. K., Wheeler M. E., Vichos E. E., Fung F. Y. Regulation of the immune response. XI-Cell-mediated feedback of an in vitro cell-mediated immune response. Cell Immunol. 1976 Dec;27(2):153–162. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(76)90224-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stobo J. D., Paul S., Van Scoy R. E., Hermans P. E. Suppressor thymus-derived lymphocytes in fungal infection. J Clin Invest. 1976 Feb;57(2):319–328. doi: 10.1172/JCI108283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson A. D., Cochrane M. A., McFarlane I. G., Eddleston A. L., Williams R. Lymphocyte cytotoxicity to isolated hepatocytes in chronic active hepatitis. Nature. 1974 Dec 20;252(5485):721–722. doi: 10.1038/252721a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twomey J. J., Laughter A. H., Farrow S., Douglass C. C. Hodgkin's disease. An immunodepleting and immunosuppressive disorder. J Clin Invest. 1975 Aug;56(2):467–475. doi: 10.1172/JCI108113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldmann T. A., Durm M., Broder S., Blackman M., Blaese R. M., Strober W. Role of suppressor T cells in pathogenesis of common variable hypogammaglobulinaemia. Lancet. 1974 Sep 14;2(7881):609–613. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)91940-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wands J. R., Perrotto J. L., Alpert E., Isselbacher K. J. Cell-mediated immunity in acute and chronic hepatitis. J Clin Invest. 1975 May;55(5):921–929. doi: 10.1172/JCI108021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wands K. R., Isselbacher K. J. Lymphocyte cytotoxicity to autologous liver cells in chronic active hepatitis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1301–1303. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Meyer zum Büschenfelde K. H., Knolle J., Berger J. Celluläre Immunreaktionen gegenüber homologen leberspezifischen Antigenen (HLP) bei chronischen Leberentzündungen. Klin Wochenschr. 1974 Mar 1;52(5):246–248. doi: 10.1007/BF01468598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


