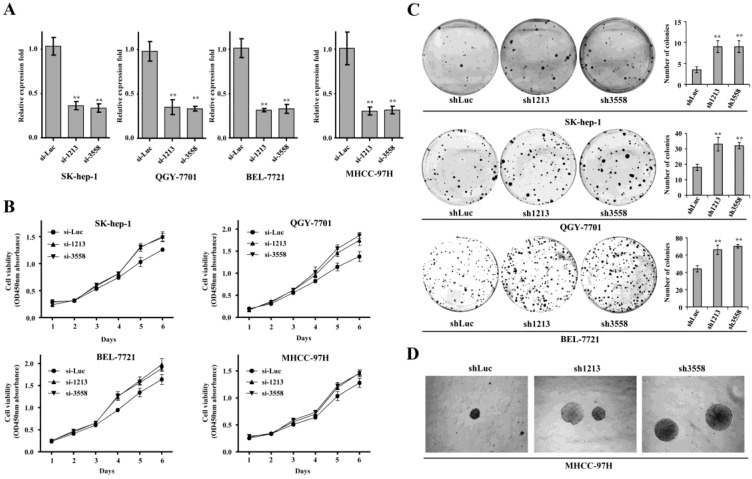
Figure 3.
SAMD9L knockdown promotes the growth and colony formation of HCC cell in vitro. (A) The efficiency of two siRNA (si-1213, si-3558) against endogenous SAMD9L was evaluated by quantitative RT-PCR assay in SK-hep-1, QGY-7701, BEL-7721 and MHCC-97H cells, where si-Luc was used as a negative control. (B) Cell growth curves were measured based on cell viability while the two siRNAs (si-1213, si-3558) were transfected into SK-hep-1, QGY-7701, BEL-7721 and MHCC-97H cells, respectively. (C) Upon SAMD9L knockdown mediated by pSUPER-sh1213 and pSUPER-sh3558 constructs, anchorage-dependent colony formation assay was performed in SK-hep-1, QGY-7701 and BEL-7721 cells. pSUPER vector carrying shLuc was used as a negative control. The histograms showed mean with standard deviation of colony numbers and statistical significance was calculated using two-tailed student's t test. *, P < 0.01; **, P < 0.01. (D) Representative microscopic photographs of anchorage-independent colony formation assay were shown in soft agar medium when SAMD9L was silenced in MHCC-97H cells. Here all experiments were performed independently 3 times.