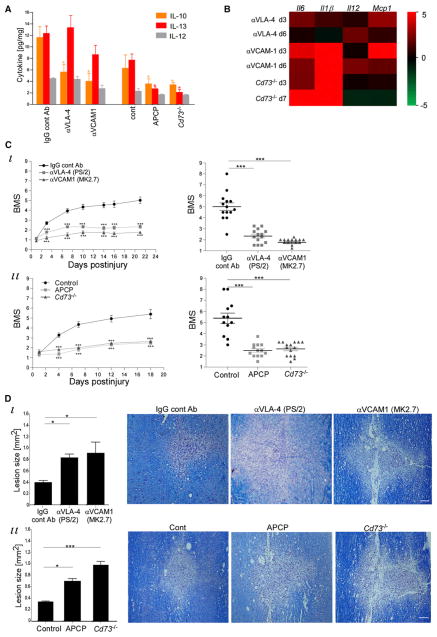
Figure 5. The CP-Dependent Recruited Cells Resolve Inflammation and Improve Recovery.
VLA-4-VCAM-1 interaction (by VLA-4 or VCAM-1 antibodies) or CD73 activity (using APCP, or Cd73−/−) was inhibited in SC-injured mice; appropriate controls were included.
(A) Cytokine Multiplex analysis of lesion site (d7). n = 4–8 pools of 3 mice. Two-way ANOVA: F5,74 = 11.1, p < 0.0001.
(B) qRT-PCR analysis of lesion sites for genes encoding proinflammatory cytokines, presented as a heat map relative to the relevant control.
(C) Hind limb motor function, assessed according to the BMS. Left: Motor score as a function of time. Right: Scores (d21) of individual mice. (i) n = 14–15 mice per group. Left: repeated ANOVA: Fbetween groups(2,40) = 60.8, p < 0.0001; right: ANOVA, F = 59, p < 0.0001. (ii) n = 12–15 mice per group. Left: repeated ANOVA: Fbetween groups(2,37) = 36.7, p < 0.0001; right: ANOVA: F = 32, p < 0.0001.
(D) Quantification of lesion size (d21; an average of 3 depths) and representative pictures, as demarcated by Luxol and Nissl reactivity in longitudinal coronal sections. n = 8–10 mice per group. ANOVA: (i) F = 35, p = 0.02; (ii) F = 10.2, p = 0.0007.
Data are represented as mean ± SEM. Scale bars represent 100 μm (D).