Fig. 1.
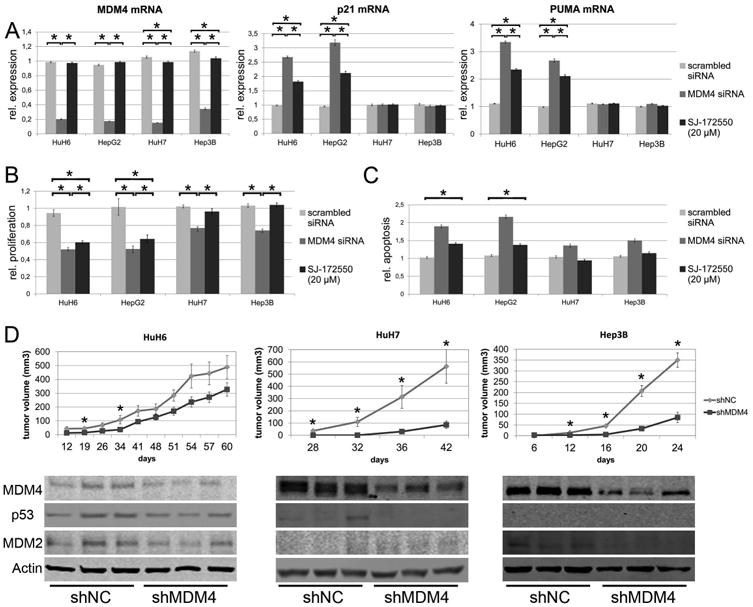
MDM4 exerts protumorigenic effects via p53-dependent and –independent mechanisms. (A) MDM4, p21, and PUMA mRNA levels following siRNA-mediated silencing of MDM4 (dark grey bars) in HuH6 (p53- wildtype), HepG2 (p53-wildtype), Hep3B (p53-deleted), and HuH7 (p53-mutated) cells and after treatment with SJ-172550 (20μM, black bars), a blocker of the MDM4-p53 interaction. Induction of p53 target genes is only observed in HCC cell lines with p53 wild-type alleles. The values shown are normalized against the transfection reagent. (B) Both siRNA-mediated silencing of MDM4 (dark grey bars) and SJ-172550 treatment (black bars) reduces proliferation and (C) increases apoptosis in HCC cells (normalized against oligofectamine-treated cells). (D) 5 × 106 cells transfected with either an shRNA targeting MDM4 (shMDM4) or a neutral control shRNA (shNC) were subcutaneously injected into the flank of NOD/SCID mice (HuH6: n=14; HuH7, Hep3B: n = 12 tumors). Tumor formation and growth was significantly reduced in shMDM4 transfected cells (upper panel; * P < .05). Reduced MDM4 expression is seen in tumor tissues derived from shMDM4 transfected HCC cells (lower panel). In addition, p53 levels are decreased in shMDM4-expressing HuH6 and HuH7 cells, while MDM2 expression is lowered in HuH6 and Hep3B cells.
