Fig. 2.
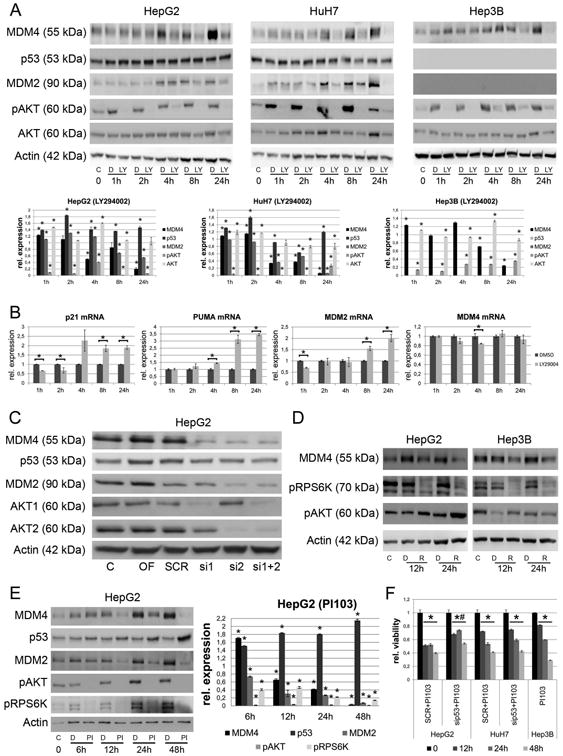
AKT and mTOR signaling are involved in the regulation of MDM4 protein expression. (A) The PI3KInhibitor LY294002 reduces the phosphorylation of AKT and the MDM4 protein levels in all three HCC cell lines in a time-dependent manner. This effect is associated with reduced MDM2 and increased p53 expression in HepG2 and HuH7 cells. Note, the p53-deficient Hep3B cells do not express the p53-target gene MDM2. The lower panel shows the results from densitometric analysis. * P < .05 (B) LY294002 treatment induces the mRNA-expression of p53 target genes (p21, PUMA, MDM2, P < .05), while the transcription of MDM4 is not significantly affected (P > .05). Dark grey bars represent DMSO treated and light grey bars represent LY294002-treated HepG2 cells. (C) Validation of the influence of AKT signaling on MDM4 protein levels by treating HepG2 cells using isoform specific siRNAs against AKT1 and AKT2. (D) The mTORC1 inhibitor Rapamycin reduces the phosphorylation of RPS6K and the MDM4 protein levels in HepG2 cells. (E) PI103 inhibits activation of both AKT- and mTOR signaling, abolishes the expression of MDM4 and MDM2 and increases the p53 level in HepG2 cells in a time-dependent manner. (F) PI103 treatment significantly reduces the cell viability in HepG2, HuH7 and Hep3B cells compared to DMSO treated cells, respectively (* P < .05). In HepG2 cells siRNA-mediated inhibition of p53 significantly reduces the effect of PI103 treatment on cell viability (# P < .05). Abbreviations: C, untreated control; D, DMSO; LY, LY294002; OF, oligofectamine control; SCR, scrambled siRNA; R, rapamycin; PI, PI103; si1, siRNA targeting AKT1; si2, siRNA targeting AKT2.
