Fig. 3.
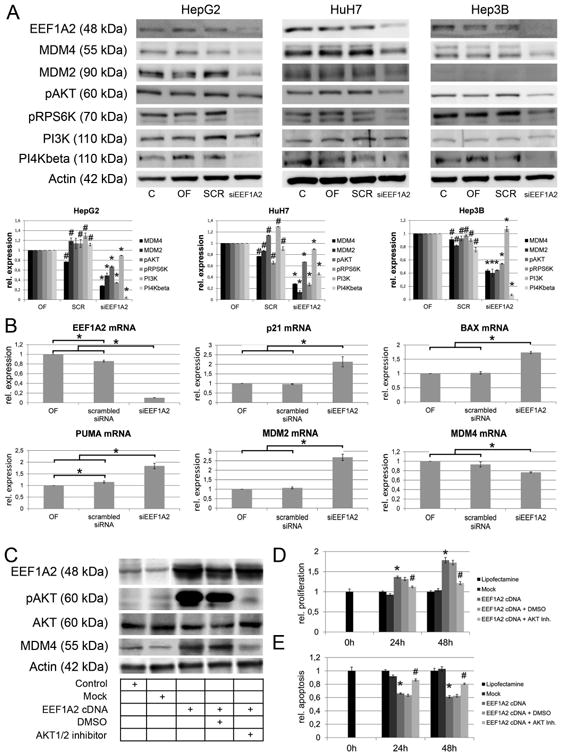
EEF1A2 is involved in the regulation of MDM4 protein expression. (A) siRNA-mediated knockdown of EEF1A2 expression diminishes the activation of both AKT- and mTOR signaling via reduction of PI4KB expression, which leads to reduced MDM4 protein expression. Upper panel: representative Western blots; lower panel: relative protein expression according to densitometric analysis of Western blots normalized against β-Actin expression and oligofectamine control. *siEEF1A2 vs. OF and SCR, P < .05; #OF vs. SCR, P < .05. (B) Reactivation of p53 function following siRNA-mediated silencing of EEF1A2 is indicated by activation of p21, BAX, puma, and MDM2 mRNA expression (P < .05). (C) Western immunoblotting following EEF1A2 cDNA transfection in HuH6 cells. The EEF1A2 induced upregulation of MDM4 can be rescued by pharmacological inhibition of AKT1/2. (D/E) Transfection of EEF1A2 increases the proliferation (D) and reduces the apoptotic rate (E), which can be partially prevented by AKT1/2 inhibition. * EEF1A2 cDNA vs. Mock, P < .05; # EEF1A2 cDNA vs. EEF1A2 cDNA + AKT1/2 inhibitor, P < .05. Abbreviations: C, untreated control; OF, oligofectamine control; SCR, scrambled siRNA; PI4KB, phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase beta; siEEF1A2, siRNA targeting EEF1A2; AKT Inh., AKT1/2 inhibitor.
