Fig. 6.
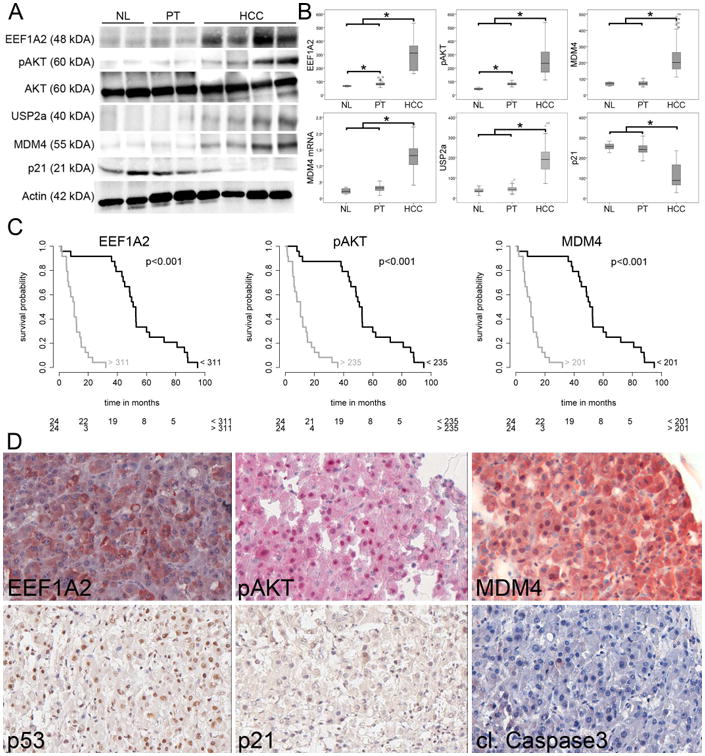
Dysregulation of the EEF1A2-AKT-MDM4 axis in human HCC. (A) Representative Western blots of lysates prepared from NL, PT, and HCC and immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. (B) Western blot optical densities were normalized to β-actin values and expressed in arbitrary units. (C) Survival probability of human HCC patients depends on the expression level of EEF1A2, pAKT, and MDM4. The number of patients at risk is indicated in the lower part of the survival plots. (D) Representative immunohistochemical stainings of the tissue microarray. High EEF1A2 expression is associated with phosphorylation and thus activation of AKT, which stabilizes MDM4. Despite nuclear p53, there is neither upregulation of p21 nor apoptosis induction (cleaved Caspase 3). Original magnification: 40×. Abbreviations: NL, normal liver, PT, peritumorous non-neoplastic liver.
