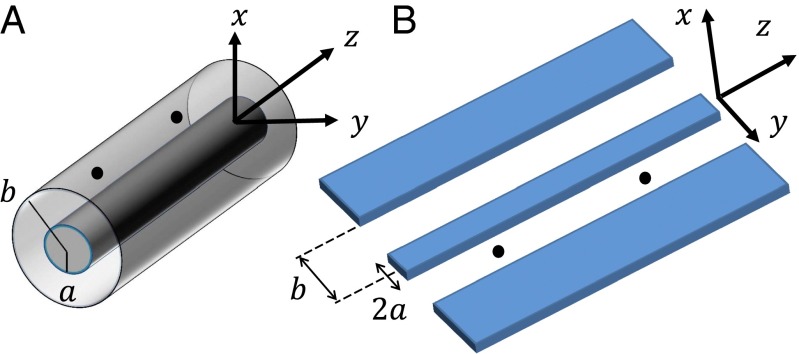
Fig. 1.
Geometries of transmission-line–mediated vdW and Casimir interactions. (A) Coaxial line: two concentric metallic cylinders, the inner one with radius a and the outer (hollow) one with radius b. Two dipoles represented by black circles are placed in between the cylinders, along the wave propagation direction z. They interact via modes of the coaxial line that are in the vacuum state, giving rise to a vdW-like interaction energy. (B) Coplanar waveguide: similar to A. Here the central conductor of width 2a is separated from a pair of ground plane conductors that are 2b apart.