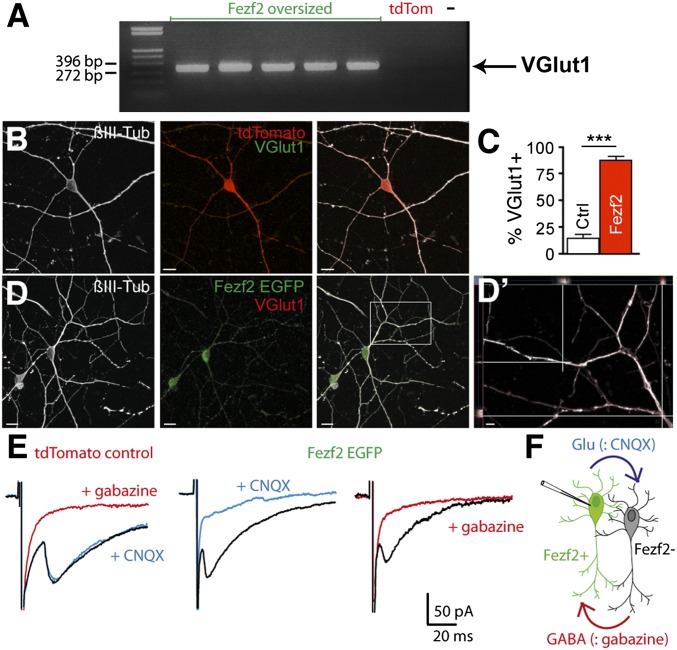
Fig. 4.
Fezf2 induces a glutamatergic phenotype. (A) Single-cell RT-PCR detection of VGlut1 (expected size = 311 bp) in Fezf2 oversized (n = 8/3 cells/mice) but not in TdTomato control (n = 5/2 cells/mice) cells. −, negative control (i.e., water). Neurosphere-derived control neurons (tdTomato, red) do not express VGlut1 (B; green), whereas Fezf2+ neurons (green) express VGlut1 (D; red). (Scale bars: B and D, 10 μm). βIII Tubulin (βIII-Tub; white) was used as a neuronal marker. (D′) Orthogonal projections show VGlut1+ particles (red) in neuronal processes (white). (Scale bar: 2 μm). (C) Total of 88.40 ± 3.003% of Fezf2+ neurons and 14.16 ± 3.136% of control neurons are VGlut1+ (n = 5 neurosphere preparations, n = 98 Fezf2+ cells vs. n = 90 control neurons, t test, ***P < 0.001). (E and F) Voltage steps (1 ms) elicited inward currents blocked by gabazine (10 μM) but not CNQX (10 μM) in control neurons 3 wk after differentiation (five of five neurons). In Fezf2+ neurons, inward currents were always blocked by either gabazine (five of five neurons) or CNQX (seven of seven neurons), suggesting that Fezf2+ neurons form glutamatergic synapses with neighboring GABAergic cells, which, in turn, releases GABA onto the patch-clamped neuron as shown in the schematic drawing (F).