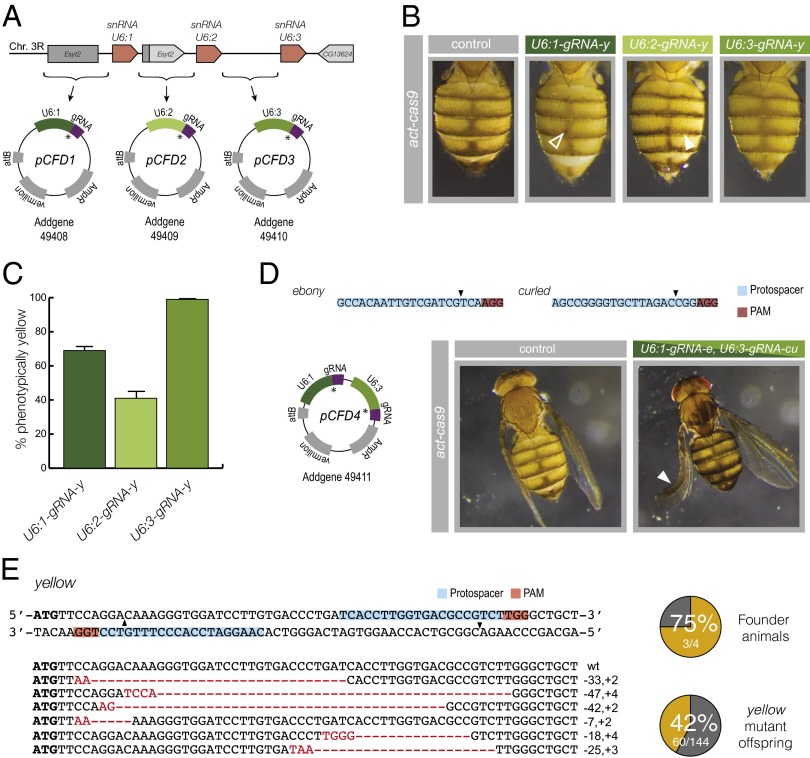
Fig. 2.
Versatile gRNA-expression vectors. (A) Schematic of the U6 locus. U6 genes are shown as orange blocks; intervening sequences and neighboring genes are shown in gray. Sequences 5′ to each U6 gene were cloned in front of a core gRNA sequence to generate plasmids pCFD1–3. The asterisk indicates positions of the BbsI cloning cassette for insertion of target sequence. (B) Differential activity of U6-gRNA constructs in epidermal cells. Female flies are shown that are heterozygous for act-cas9 and a gRNA-y transgene under the control of the U6:1, U6:2, or U6:3 promoter. Lighter body coloration indicates CRISPR/Cas-mediated mutagenesis of the two wild-type y alleles present in these flies. Arrowheads show examples of wild-type pigmentation with the U6:1 promoter and mutant pigmentation with the U6:2 promoter. (C) Mean germ-line transmission rates using different gRNA transgenes. nos-cas9 U6-gRNA-y females were crossed to y mutant males, and y mutant offspring were counted (three crosses per genotype). Displayed values are adjusted to account for the 25% of y mutant offspring expected in the absence of mutagenesis. Error bars represent SEM. (D) Targeting of two genes in the same animal with a double gRNA vector, pCFD4. Representative images are shown of flies that express act-cas9 in the absence or presence of a single transgene expressing gRNAs to e and cu. The arrowhead indicates the curled wing of a fly with extensive ebony pigmentation. (E) pCFD4 allows mutagenesis by offset-nicking in combination with act-cas9D10A. (Upper Left) Target sites of gRNAs (arrowheads indicate location of nicks). (Right) Summary of results from injecting pCFD4 encoding the two y gRNAs into transgenic act-cas9D10A embryos and crossing to y flies to assess germ-line transmission of loss-of-function y alleles. In these and other figures, “founder” refers to an animal that transmitted mutant alleles to the next generation. In the four crosses, 22 of 22 files, 11 of 56 flies, 27 of 31 files, and none of 35 flies inherited a nonfunctional y allele. (Lower Left) Sequence of six different indels found in 20 analyzed yellow progeny.