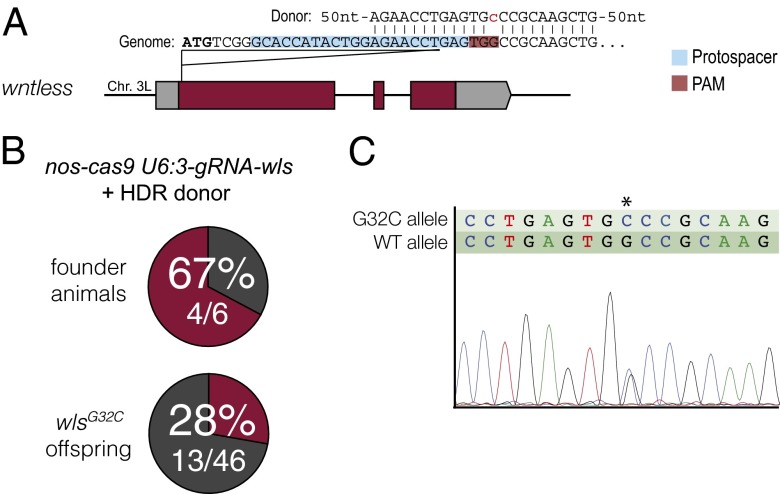
Fig. 4.
Efficient incorporation of an exogenous sequence in wls by HDR following Cas9-induced DSBs. (A) Schematic of the donor DNA in relation to the gRNA target site at the wls locus. The donor was a single-stranded oligonucleotide with 60-nt homology to the wls locus at either side of the Cas9 cut site and a G-to-C transversion (red, lowercase) that disrupts the PAM sequence. Donor DNA was injected into embryos that were the progeny of nos-cas9 females and U6:3-gRNA-wls males. (B) Summary of results from screening flies for HDR events by PCR and sequencing. In the six crosses, none of eight flies, two of eight flies, three of eight flies, six of seven flies, none of seven flies, and two of eight flies inherited the wlsG32C allele. (C) Example of the verification of the precise integration of the donor DNA in the wls locus by direct sequencing of a PCR product amplified from a heterozygous fly. Double peaks in the chromatogram represent an overlay of the sequence from the mutant and wild-type wls alleles. The asterisk indicates the position of the mutation.