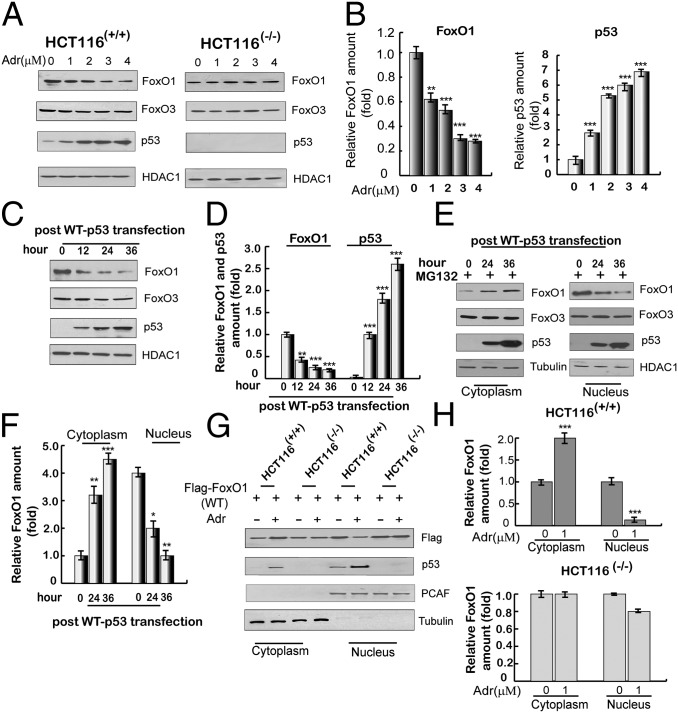
Fig. 2.
Activation of p53 promotes translocation of FoxO1 from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. (A) Adriamycin-induced expression of FoxO1 and FoxO3 proteins in HCT116(+/+) and HCT116(−/−) cells. Nuclear extracts were subjected to immunoblotting with indicated antibodies at 12 h after treatment with indicated concentrations of adriamycin. HDAC1 was used as a loading control. (B) Quantitation of FoxO1 and p53 expression levels. Immunoblots in A were scanned and normalized to HDAC1. (C) Ectopic p53-induced expression of nuclear FoxO1 and FoxO3 in HCT116(−/−) cells. Cells were transfected with an empty plasmid or a plasmid expressing p53, and nuclear extracts were analyzed by immunoblotting with indicated antibodies. (D) Quantitation of FoxO1 and p53 expression levels. Immunoblots in C were scanned and normalized to HDAC1. (E) Nuclear versus cytoplasmic localization of FoxO1 and FoxO3 following ectopic p53 expression in HCT116(−/−) cells. Subcellular fractions were analyzed by immunoblotting at 24 h or 36 h after transfection with an empty plasmid or a plasmid expressing p53 in the presence of MG132 (2 μM, for 12 h). (F) Quantitation of relative levels of cytoplasmic and nuclear FoxO1. Immunoblots in E were scanned and normalized to HDAC1. (G) p53 induction-dependent redistribution of ectopic FoxO1 in HCT116(+/+) and HCT116(−/−) cells. Cells were transfected with flag-tagged FoxO1 in the presence or absence of adriamycin (1 μM, for 12 h before harvest, and the same for below). At 36 h posttransfection, cytoplasmic and nuclear lysates were subjected to immunoblotting with antibodies indicated on the right. PCAF and tubulin were used as loading controls for nuclear and cytosolic proteins, respectively. (H) Quantitation of relative amounts of cytoplasmic and nuclear flag-FoxO1. Immunoblots in G were scanned and normalized to either PCAF or tubulin. All data above are shown as the mean ± SD, n = 3. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001.