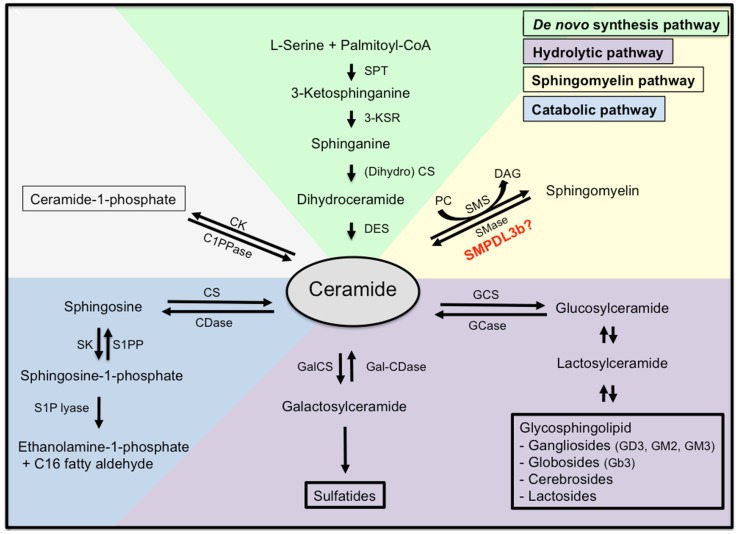
Figure 2.
Sphingolipid metabolism. Ceramide is the centerpiece of the sphingolipid metabolic pathway and can be synthesized de novo from l-serine and palmitoyl-CoA (green), through hydrolysis of sphingomyelin (yellow), or through hydrolysis of glycosphingolipids and sulfatites (purple). Ceramide can also be synthesized from sphingomyelin through the action of sphingomyelinases, or from ceramide-1-phosphate through the action of ceramide-1-phosphate phosphatase. Finally, ceramide can be further catabolized (blue) to sphingosine and sphingosine-1-phosphate, which are biologically active metabolites and finally to ethanolamine-1-phosphate and C16 fatty aldehydes. SPT, serine palmitoyl transferase; 3-KSR, 3-ketosphinganine reductase; CS, ceramide synthetase; DES, dihydroceramide desaturase; SMase, sphingomyelinase; SMS, sphingomyelin synthetase; PC, phosphatidylcholine; DAG, diacylglycerol; C1PPase, ceramide-1-phosphate phosphatase; CK, ceramide kinase; CDase, ceramidase; CS, ceramide synthase; SK, spingosine kinase; S1PP, spingosine-1-phosphate phosphatase; GCS, glycosylceramide synthase; GCase, glycosylceramidase; GalCS, galactosylceramide synthase; Gal-CDase, galactosylceramidase.