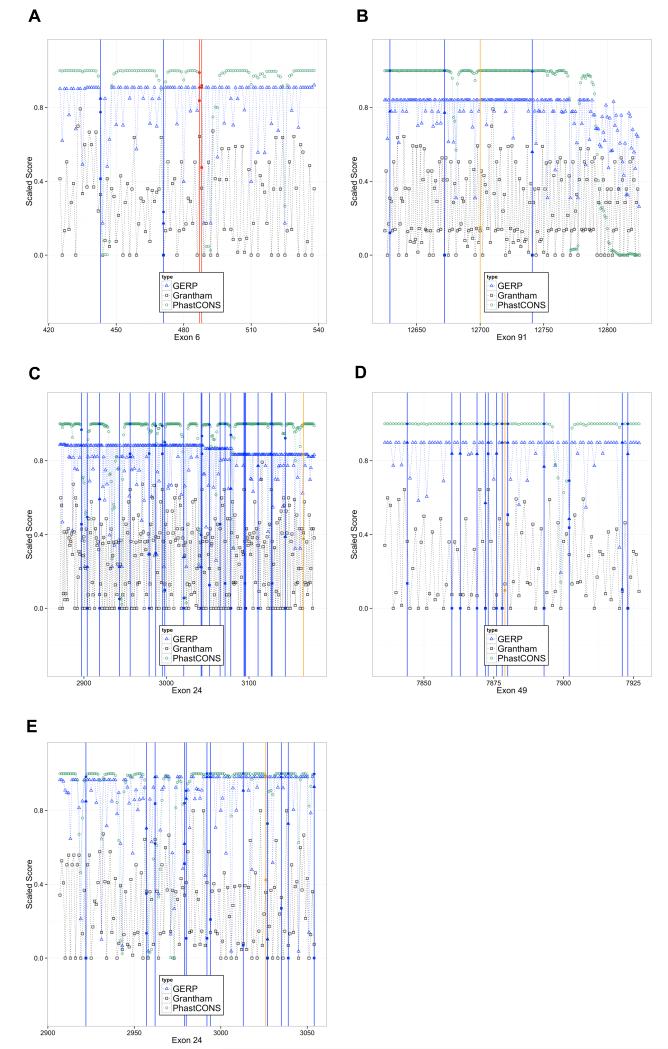
Fig. 5.
Gene conservation scores graphed for RYR1 and CACNA1S exons
GERP++, Grantham, and PhastCons scores are displayed for four RYR1 exons and oneCACNA1S exon. All scores were scaled to fit within a 0-1 scale on the vertical axis for ease of viewing. Blue vertical lines mark positions were variants were seen in 5,379 UW ESP exomes, red vertical lines mark an EMHG causal variant, and orange lines mark a rare variant found in one of four families in this study. A) RYR1 exon 6, showing two EMHG pathogenic variants and two UW ESP variants; B) RYR1 exon 91 which has the Family A variant; C) RYR1 exon 24 which has the Family B variant; D) RYR1 exon 49 which has the Family G variant; E) CACNA1S exon 24, which has the Family C variant.
Calcium channel, voltage-dependent, L type, α1S subunit gene= CACNA1S;European Malignant Hyperthermia Group = EMHG; Exome Sequencing Project = ESP; genomic evolutionary rate profiling = GERP; ryanodine receptor 1 gene= RYR1; University of Washington = UW.