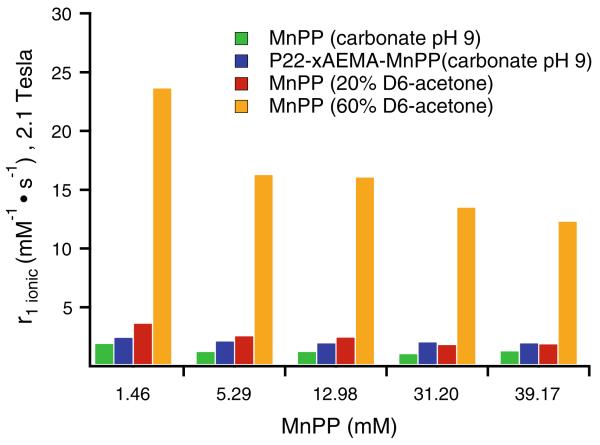
Fig. 8.
Ionic relaxivities at different concentrations of free MnPP compared with P22-xAEMA-MnPP in carbonate pH 9 buffer (see Table S1 for the corresponding loading factors). The free MnPP was further treated with either 20 or 60 % acetone-D6 to try to disperse the MnPP molecules and see the impact of acetone on the relaxivity. MnPP (green bars) at the same local concentrations of MnPP as for P22-xAEMA-MnPP (blue) exhibits similar r1,ionic values, with those for free MnPP being slightly smaller than those for P22-xAEMA-MnPP. After free MnPP had been treated with 20 % acetone-D6 (red bars), the ionic relaxivities did not change much, increasing only slightly for the lower concentrations. At 60 % acetone-D6 (orange bars), a dramatic increase in ionic relaxivity was observed at all concentrations, with a trend toward the highest increase in relaxivity for the lowest concentration of MnPP